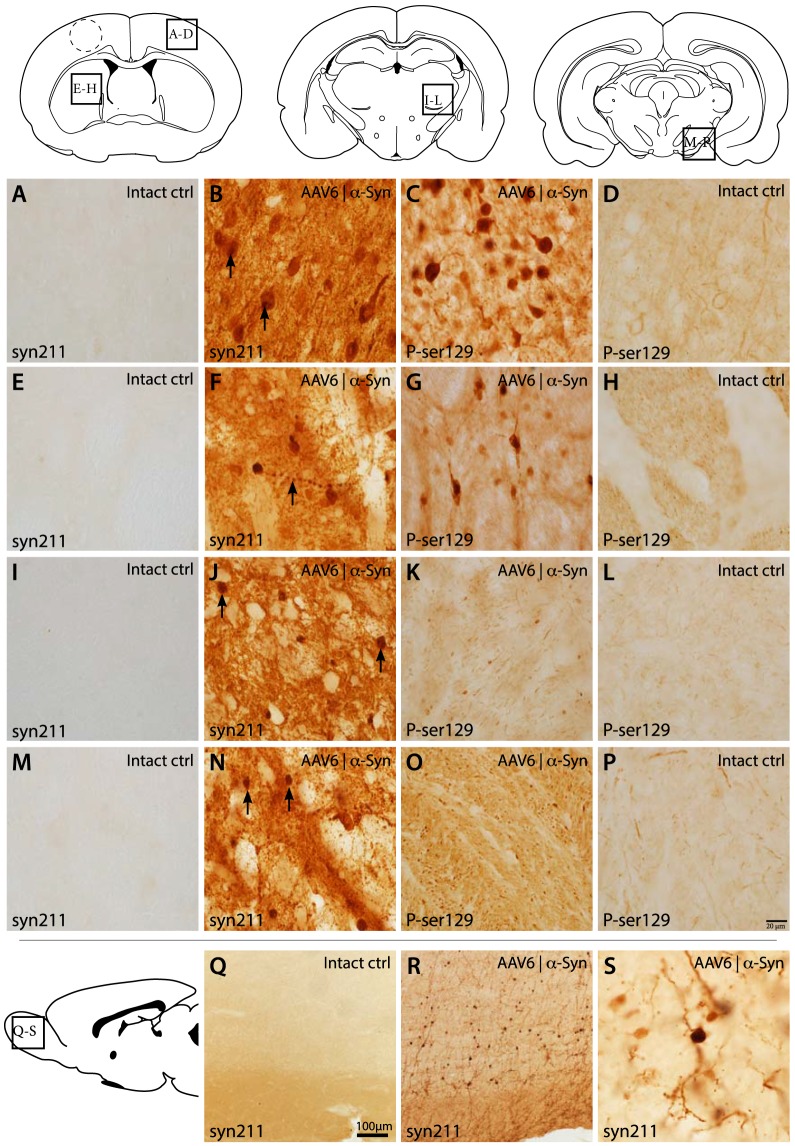
Figure 4. High-power histological analysis of α-synuclein expression.
Histological analysis of the cerebral cortices revealed high expression of human α-synuclein (syn211) within the soma and axonal projections of the cortical neurons. These neurons displayed a high incidence of α-synuclein punctates within their soma (arrows), while phosphorylated α-synuclein (P-ser129) was highly increased within the neuronal soma, and to a lesser extent within the axonal projections (A–D). Striatal analysis revealed high incidence of neurons with prominent expression of human α-synuclein, with Lewy neurite's being a common find (arrow). Phosphorylation of α-synuclein within the striatal neurons was also upregulated (E–H) Projections within the thalamic nuclei were found to contain high levels of human α-synuclein with large α-synuclein positive structures, believed to be large axonal swellings, were present throughout the thalamus (arrows) (I–L). Large axonal swellings were also present to a large extent in the SNpR (arrows) while phosphorylation of α-synuclein appeared as only moderately increased (M–P). The neonatal injection of the AAV6 serotype displays an interesting ability to also infect neuronal progenitors within the rostral migratory stream (RMS) or the sub-ventricular zone. This is seen as mature neurons within the olfactory bulb expressing high levels of human α-synuclein (R–S). These neurons appear with healthy morphology with α-synuclein distributed throw-out the neuropil (S). Dotted lines within the cerebral cortex denote the position of the tissue punch taken for TEM analysis.