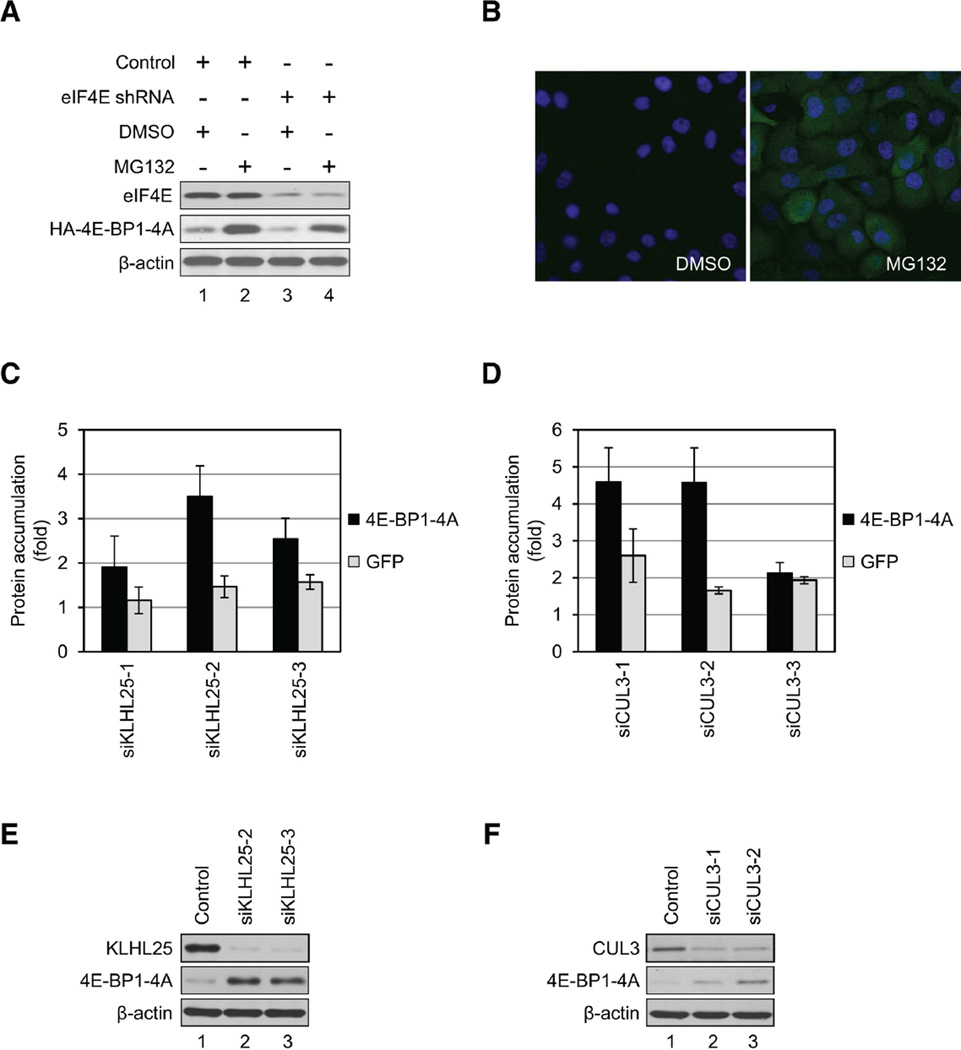
Figure 4.
KLHL25-CUL3 Ubiquitin Ligase Targets the Hypophosphorylated Form of 4E-BP1 for Degradation. (A) Generation of stable cell lines expressing 4E-BP1-4A using control or eIF4E-KD cells is shown. Cells were treated with DMSO or 5 µM MG132 for 3 hr. eIF4E, 4EBP1-4A, and β-actin levels were analyzed by western blotting. (B) 4E-BP1-4A was stabilized in eIF4E-KD cells by MG132 treatment. eIF4E-KD cells expressing 4E-BP1-4A were treated with either DMSO (left panel) or 5 mM MG132 (right panel) for 3 hr. Accumulation of 4E-BP1-4A was analyzed by immunofluorescence. Cells were fixed, and HA-4E-BP1-4A was determined with anti-HA antibody and Alexa Fluor 488 anti-rabbit IgG (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C and D) eIF4E-KD cells expressing either 4E-BP1-4A or GFP were transfected with siRNAs targeting KLHL25 (C) or CUL3 (D). Accumulation of 4E-BP1-4A (black bars) and GFP (gray bars) was determined by microscopy. Each sample was normalized against samples treated with the nonspecific siRNAs. Data are mean ± SD of two separate experiments. (E and F) 4E-BP1-4A levels are restored by siRNAs targeting KLHL25 (E) and CUL3 (F). To confirm the results obtained by the high-content screening, the KD efficiencies of both KLHL25 (E) and CUL3 (F) and 4E-BP1-4A levels were determined by western blotting. See also Figure S2 and Tables S3 and S4.