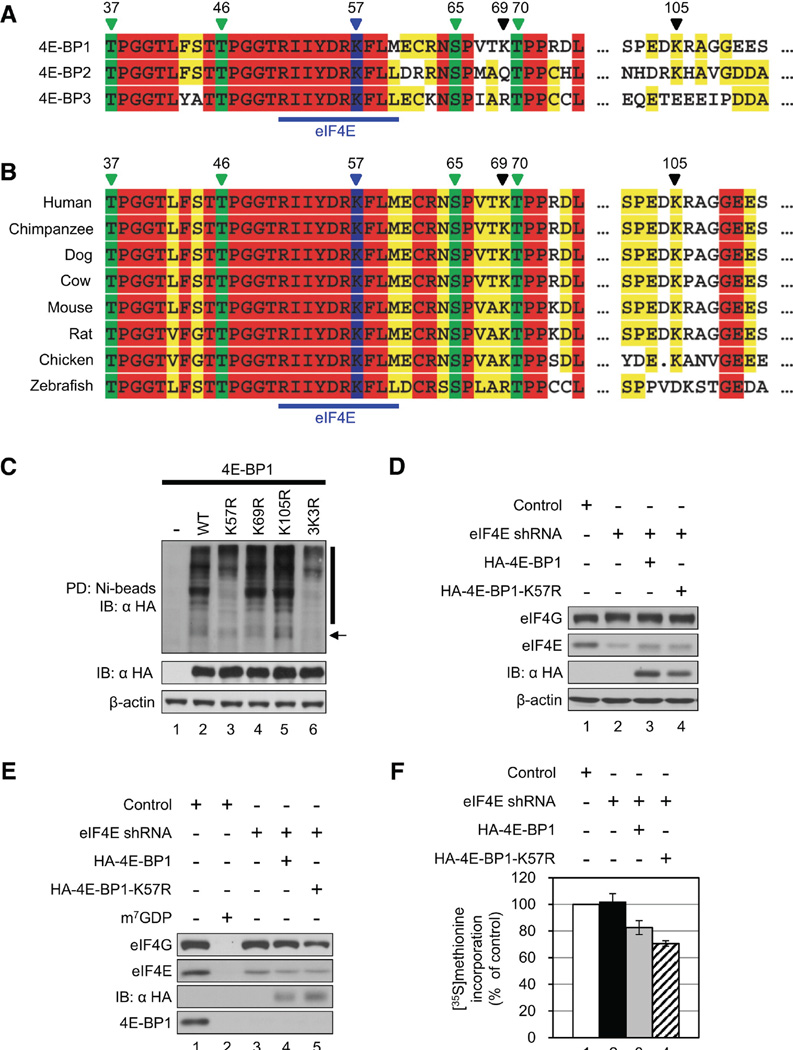
Figure 6.
Lys57 Is the Most Probable Ubiquitination Site of 4E-BP1. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of human 4E-BPs is shown. Four phosphorylation sites (Thr37, Thr46, Ser65, and Thr70) are marked in green, and the putative ubiquitination site (Lys57) is marked in blue. A blue bar indicates the eIF4E-binding site. Numbers above indicate amino acids. (B) Phylogenetic amino acid sequence alignment of 4E-BP1. (C) Lys57 is the likely ubiquitination site of 4E-BP1. HAtagged 4E-BP1, 4E-BP1-K57R, 4E-BP1-K69R, 4E-BP1-K105R, or 4E-BP1-3K3R was expressed in 4E-BP DKO MEFs along with His-Ub. An in vitro ubiquitination assay was performed as described before. Expression levels of HA-4E-BP1s and β-actin in cell lysates are shown below. An arrow and a bar indicate mono-ubiquitinated and polyubiquitinated 4E-BP1, respectively. (D) HA-4E-BP1 or HA-4E-BP1-K57R was transiently expressed in eIF4E-KD cells. eIF4G, eIF4E, HA-4E-BP1s, and b-actin levels were determined by western blotting. (E) eIF4F complex formation in cells expressing the nonubiquitinatable 4E-BP1. Cell lysates were subjected to m7GDP pull-down. One millimolar m7GDP was added as a competitor (lane 2). m7GDP-associated proteins were assessed by western blotting. (F) The effect of the nonubiquitinatable 4E-BP1 on protein synthesis is shown. Control (white), eIF4E-KD (black), eIF4E-KD cells expressing HA-4E-BP1 (gray) or HA-4EBP1-K57R (hatched) were subjected to [35S]methionine metabolic labeling. The value in control was set as 100%, and data are mean ± SD of three separate experiments. IB, immunoblot; PD, pull-down. See also Figure S3.