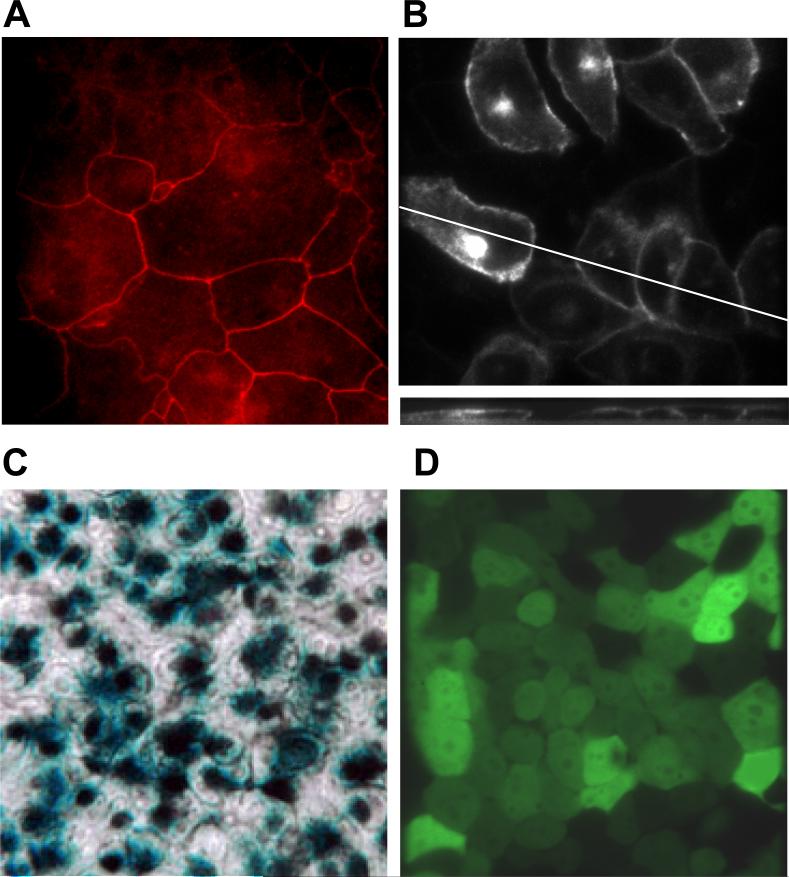
Fig. 6. Tight junctions, CFTR localization and adenoviral infections of CF15 cells.
A. ZO-1 staining of fixed CF15 cells grown as a monolayer indicates the presence of tight junctions and their position around the apical regions of cells. B. CFTR localizes to the apical pole of CF15 cells grown on cover glasses. CF15 cells were grown on cover glasses, infected with CFTR-GFP adenovirus and localization was analyzed after 24 hours by confocal microscopy. The upper panel shows a representative XY scan close to the apical membrane. The lower section represents a XZ scan at 0.5 μm increments. C. Xgal staining demonstrates success of viral infection. CF15 cells were grown on filters and infected with lacZ-adenovirus (100 MOI) for 48 hrs (apical and basolateral surfaces). Cells were fixed, treated with 1 mg/ml xgal and incubated for 18 hrs at 37° C. The light microscopy image acquired using Nomarski optics (40 × objective) shows a representative field of six independent experiments. D. EGFP-adenovirus confirms infection efficiency. CF15 cells were grown on cover glasses and infected with EGFP-adenovirus (100 MOI) for 12 hours. Confocal image was taken 24 hours post infection on cells grown to complete confluency (excitation 488 nm, 40× objective).