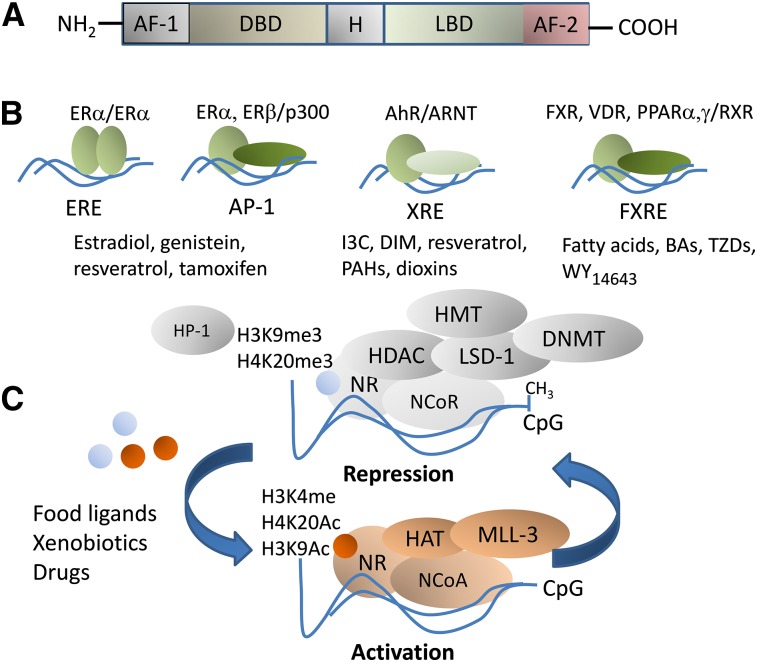
FIGURE 1.
Nuclear receptor structure and coregulation by food ligands and nutritionally related xenobiotics and drug compounds. NRs share a general DNA structure comprising an amino-terminal AF-1, an H, an LBD, and a C-terminal AF-2 domain (A). Examples of NR interactions within the coregulator interaction domains: the ERα forms homodimers at EREs; the ERα and ERβ can enhance or repress, respectively, transcription of genes containing AP-1 sites through interactions with DNA-bound Jun/Fos complexes; the AhR/ARNT heterocomplex binds DNA at XREs; the FXR forms heterodimers with the RXR at FXRE (B). Certain NRs function as promiscuous partners for various receptors. This is the case for the RXR that forms complexes at target promoters with FXR and PPAR, VDR, and retinoic acid receptor. Examples of food ligands are listed below each NR. The diagram depicts general models of repression and activation via CpG methylation and demethylation mediated by NRs (C). In the absence of ligands or when NRs are bound to antagonists, NRs are found in NCoR complexes with factors that possess DNMT and HDAC, HMT, and histone demethylase (e.g., LSD-1) properties. Certain covalent modifications placed by NR corepressors on histones are markers of silenced heterochromatin and include H3K9me3, histone 3 trimethylated at lysine 27, and H4K20me3. Chromatin is occupied by the repressive HP-1 factor. Binding of food ligands to NRs triggers the dismissal of NCoR complexes and the recruitment at the target promoter of NCoA complexes that comprise HMT (e.g., MLL-3) and HAT (e.g., cAMP-response element-binding protein/p300) factors. The latter possess enzymatic activities that place “active” histone acetylation marks on histones 3 and 4 (H3K9Ac, H4K20Ac). AF-1, activation function 1; AF-2, activation function 2; AhR, aromatic hydrocarbon receptor; AP-1, activator protein-1; ARNT, aromatic hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator; BA, bile acid; CpG, cytosine-phosphate-guanine; DBD, DNA binding domain; DIM, diindolylmethane; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; ERE, estrogen response element; ERα, estrogen receptor-α FXR, farnesoid X receptor; FXRE, farnesoid X receptor response element; H, hinge region; HAT, histone acetyltransferase; HDAC, histone deacetylase; HMT, methyltransferase; HP-1, heterochromatin protein-1; H3K4me4, histone 3 methylated at lysine 4; H3K9me3, histone 3 trimethylated at lysine 9; H4K20me3, histone 4 trimethylated at lysine 20; 3C, indol-3-carbinol; LBD, ligand-binding domain; LSD-1, lysine-specific demethylase-1; MLL-3, mixed lineage leukemia-3; NCoA, nuclear receptor coactivator; NCoR, nuclear corepressor; NR, nuclear receptor; PAH, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; TZD, thiazolidinedione; VDR, vitamin D receptor; WY14643, 2-[[4-chloro-6-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino]-2-pyrimidinyl]thio]acetic acid; XRE, xenobiotic response element.