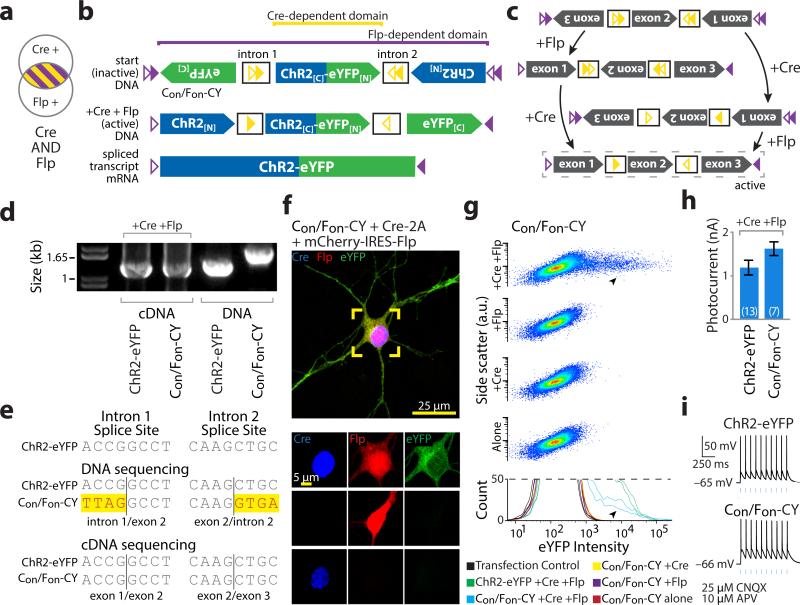
Figure 3. INTRSECT: diverse recombinases with engineered introns enable intersectional targeting in vitro.
a,b) Schematics representing (a) cells targeted by nesting Cre-dependent directional control of a central exon and Flp-dependent directional control of all three exons (b top), such that both recombinases are necessary for all exons of the construct (Con/Fon-ChR2-eYFP) to be in the sense direction (b bottom). c) Intermediate configurations in the activation of Con/Fon-ChR2-eYFP. d) cDNA prepared from HEK293 cells transfected with indicated constructs and recombinases and source DNA were amplified using primers in exons 1 and 3 and separated by gel electrophoresis. Note size difference in bands from intron-containing DNA and uniformity of cDNA bands, suggesting successful splicing. e) Sequences of bands from d. Yellow denotes difference from ChR2-eYFP map sequence, representing intron sequence. f) eYFP is only expressed in the presence of both Cre and Flp in cultured neurons transfected with Con/Fon-ChR2-eYFP (green), Cre (blue), and Flp (red) (see Supplementary Fig. 8). g) Flow cytometry dot plot (top) and biological replicate histograms (bottom) of HEK293 cells transfected with indicated recombinase/construct combinations. YFP expression is only seen with Con/Fon-ChR2-eYFP and both Cre and Flp (arrowheads; 100% of norecombinase, Cre-alone, and Flp-alone transfections fit by a single curve, 100% of Cre/Flp co-transfections fit by multiple curves). h,i) Whole cell photocurrents (h) and action potentials (i) recorded from primary neurons transfected with ChR2-eYFP or Con/Fon-ChR2-eYFP and Cre/Flp indicate robust ChR2 function comparable to native ChR2 (ChR2-eYFP: 1120±187 pA, n=6, Con/Fon-ChR2-YFP: 1621±157 pA, n=7 p=0.3542: two-sided unpaired t-test); all error bars s.e.m.