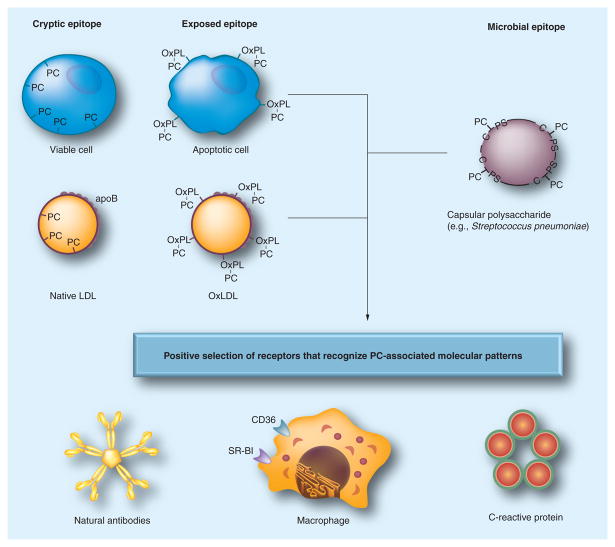
Figure 2. Pattern recognition of oxidation-specific DAMPs and microbial PAMPs.
Using the example of the PC epitope, this diagram illustrates the hypothesis of the emergence and positive selection of multiple PRRs that recognize common epitopes, shared by modified self and microbial pathogens. Oxidation of plasma membrane phospholipids in apoptotic cells alters the conformation of the PC head group, yielding an exposed epitope, accessible to recognition by macrophage scavenger receptors, NAbs and CRP. These PRRs were selected to clear apoptotic cells from developing or regenerating tissues. Recognition by the same receptors of the PC epitope of capsular polysaccharide in Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., S. pneumoniae), which is not part of a phospholipid, strengthened positive selection of these PRRs and probably helped to select additional strong proinflammatory components to PRR-dependent responses. Oxidized lipoproteins, prevalent in humans as a result of dyslipidemia and impact of environmental factors and in experimental animals, carry OxPLs with the PC epitope exposed in an analogous manner to that of apoptotic cells, which leads to recognition by PRRs and initiation of innate immune responses. The balance between proinflammatory responses of cellular PRRs and atheroprotective roles of NAbs plays an important role in the development of atherosclerosis. Modified and reproduced with permission from reference [4].