Figure 6.
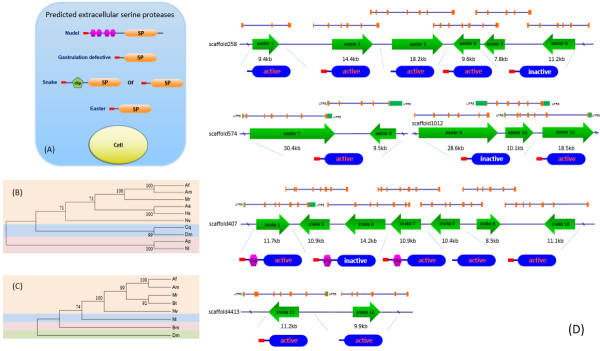
Predicted extracellular serine proteases in N. lugens . (A) The nudel-like, gastrulation defective (Gd), snake and easter genes commonly contain a putative signal peptide and a serine protease domain, which suggest the extracellular serine proteases. Red bars, pink hexagons, green pentagons and orange oblongs indicate the putative signal peptide sequence, LDLa domain, clip domain and serine protease domain with the catalytic triad, respectively. (B) Phylogenetic analyses of the insect nudel-like genes using the program Mega 5.05 as described in Figure 4. The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences are as follows: Nl, Nilaparvata lugens (KJ512077); Ap, Acyrthosiphon pisum (XP_001944581); Af, Apis florea (XP_003691528); Am, Apis mellifera (XP_006559739); Mr, Megachile rotundata (XP_003703613); Nv, Nasonia vitripennis (XP_003424379); Dm, Drosophila melanogaster (NP_523947); Cq, Culex quinquefasciatus (XP_001843380); Ae, Acromyrmex echinatior (EGI57358); Hs, Harpegnathos saltator (EFN86687). (C) Phylogenetic analyses of the insect Gd genes. The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences are as follows: Nl, Nilaparvata lugens (KJ512078); Af, Apis florea (XP_003690498); Am, Apis mellifera (XP_006563318); Mr, Megachile rotundata (XP_003704669); Bt, Bombus terrestris (XP_003402764); Nv, Nasonia vitripennis (XP_003427708); Bm, Bombyx mori (XP_004929031); Dm, Drosophila melanogaster (NP_511134). (D) Structure and location of the easter and snake genes on scaffolds. The green arrows indicate the transcription orientations and gene sizes on the scaffolds. The exons and the 5′ and 3′ UTR regions are shown with orange and green boxes, respectively. The deduced protein structures are shown under the genomic structures. Red bars and blue oblongs indicate the putative signal peptide sequence and serine protease domain that contains the complete or incomplete catalytic triad, respectively.
