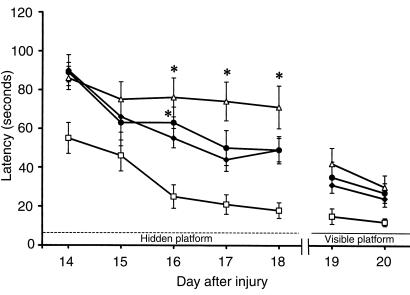
Figure 4.
The effects of TBI with secondary hypoxemic insult and treatment with iNOS inhibitors on MWM performance in rats. Mean latencies (± SEM) to find a submerged (hidden) platform on days 14–18 after TBI. All injured groups had the longest (most impaired) latencies on day 14 after injury. However, rats treated with either of the iNOS inhibitors (AG or L-NIL) exhibited persistently higher latencies to find the platform on days 16, 17, and 18 after injury, compared with sham (open squares). Shown are saline (filled diamonds), AG (filled circles), and L-NIL (open triangles) treatments. *P < 0.05 vs. sham. Improved performance on visible-platform testing (compared with hidden-platform testing) done on days 19–20 indicates that the deficits seen were not caused by visual impairment.