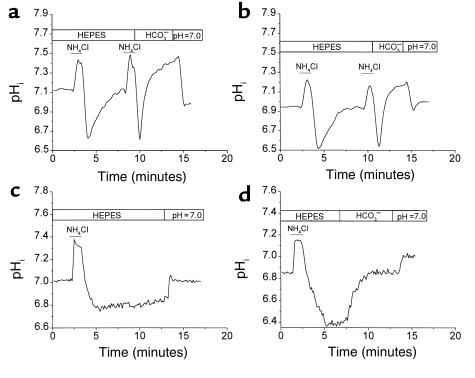
Figure 2.
Examination of recovery from acid loading in both WT and NHE1 mutant CA1 neurons in the presence and absence of CO2/HCO3–. (a) CO2/HCO3– enhances the recovery from an acid load in a WT CA1 neuron. A single CA1 neuron was acid-loaded twice with HEPES solution containing 20 mM NH4Cl. The cell was allowed to recover first in the absence, and then in the presence, of CO2/HCO3–. This WT cell promptly recovered from the acid load in both solutions, and with a faster recovery rate when the CO2/HCO3– was present. (b) CA1 neurons isolated from NHE1 mutant mice exhibit different patterns of pHi recovery from acid load. Although recovery from acid loads was present in this mutant neuron, the rates in the presence or absence of CO2/HCO3– were lower than in the WT. (c) Another mutant neuron was studied. In this experiment, the mutant neuron does not recover in HEPES buffer, even 10 minutes after acid loading. (d) With CO2/HCO3–, pHi of this kind of mutant cell recovers from acid loading to the starting level, albeit at a much reduced rate. At the end of each experiment, the cell was exposed to nigericin calibration solution (pH = 7.0) for calibration.