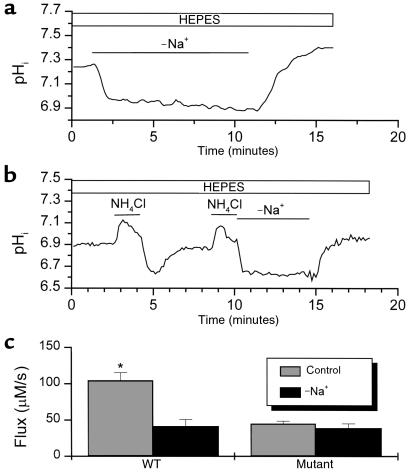
Figure 5.
Na+ dependency of pHi regulation in WT and mutant CA1 neurons. (a) The effect of Na+ removal on the steady-state pHi regulation in a WT neuron. Each neuron was studied in HEPES buffer and in a non–Na+-containing HEPES buffer. Steady-state pHi fell and remained at a low level until the external solution was switched back to standard, Na+-containing HEPES buffer. (b) The effect of Na+ removal on the recovery from acid load in a WT neuron. The neuron was acid-loaded twice in this experiment. After the first acidification, the neuron was allowed to recover in a standard Na+-containing HEPES buffer. The pHi of the cell recovered to baseline. The recovery, however, was blocked when the neuron was exposed to a non–Na+-containing HEPES buffer after the second acidification. (c) Summary of 11 experiments in WT neurons and 14 experiments in mutant neurons. In non–Na+-containing HEPES solution, a significant reduction (at pH range of 6.5–6.9) in H+ flux was observed in WT neurons but not in mutant neurons. *P < 0.05.