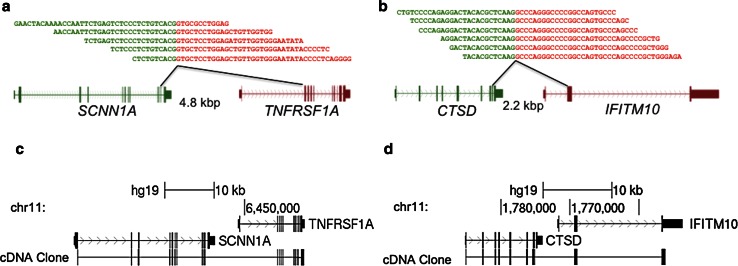
Fig. 1.
Breast cancer associated read-through fusion transcripts. Two breast cancer associated read-through fusion transcripts, SCNN1A-TNFRSF1A (a) and CTSD-IFITM10 (b), were detected in paired-end RNA-seq performed on breast cancer cell lines and primary tumors and were not detected in a variety of non-neoplastic human tissues. The 5′ gene partner is depicted in green, and the 3′ gene partner is depicted in red. The fusion transcripts use endogenous splice sites to fuse the two transcripts and the angled black lines indicate which exons flank the fusion junction to result in the chimeric transcript. RNA-seq reads that span the fusion junction are depicted above the gene models and the sequence from the 5′ partner is in green text and the sequence from the 3′ partner is in red text. The intergenic chromosomal distance between the fusion partners is denoted in kilobase pairs (kbp). Breast cancer cell line cDNA was PCR amplified using primers in the distal ends of the partner genes, and clones were sequenced. The alignment of the cDNA to the genome and the canonical gene models at this locus are depicted for SCNN1A-TNFRSF1A (c) and CTSD-IFITM10 (d). Both fusion transcripts include all of the canonical exons and splice sites of the partner genes up to the fusion junction and the fusion junction maintains the reading frame of the canonical transcripts