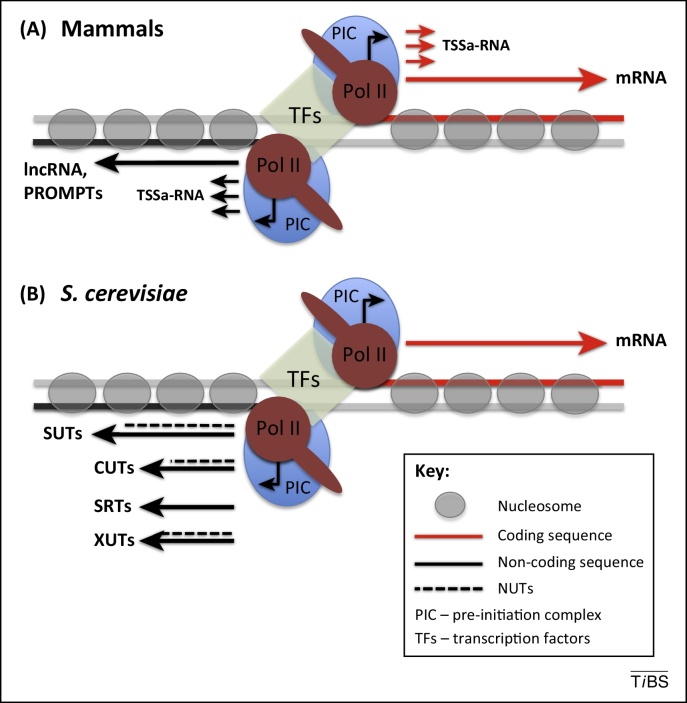
Figure 1.
Promoter-associated noncoding RNA. (A) Major classes of promoter-associated ncRNA in animals. (B) ncRNA transcribed from divergent promoters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. NFR acts as a Pol II promoter for both the protein-coding sequence (marked as a red line) and antisense noncoding sequence (black line). The open and unbiased nature of NFR allows for formation of two independent PICs, which share TFs. Such promoter structure allows Pol II to transcribe in both directions. In mammals the upstream regions are transcribed into PROMPTs and longer ncRNA generally referred to as lncRNA. TSSa-RNA, related to Pol II pausing, are synthesized in both directions. S. cerevisiae bidirectional promoters for protein-coding genes are similarly used to initiate transcription of upstream noncoding regions. Transcribed ncRNA are classified as SUTs, CUTs, or XUTs by their susceptibility to different degrading enzymes (Box 1). SRTs are synthesized when interactions between the promoter and the sense open reading frame terminator is disrupted. All ncRNA initiated from Pol II promoters, except for SRTs, may undergo NRD dependent termination and so are classified as NUTs (marked by dotted line). The most common classes of promoter-associated ncRNA are SUTs and CUTs, whereas occurrence of SRTs and XUTs is similar. Due to the lack of Pol II promoter pausing TSSa-RNA are not present in S. cerevisiae. Abbreviations: CUT, cryptic unstable transcript; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; ncRNA, noncoding RNA; NFR, nucleosome-free region; NRD, NRD complex; NUT, Nrd1-dependent unterminated transcript; PIC, preinitiation complex; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; PROMPT, promoter upstream transcript; SRT, Ssu72-restricted transcript; SUT, stable unannotated transcript; TF, transcription factor; TSSa-RNA, transcription start site-associated RNA; XUT, Xrn1-depednent transcript.