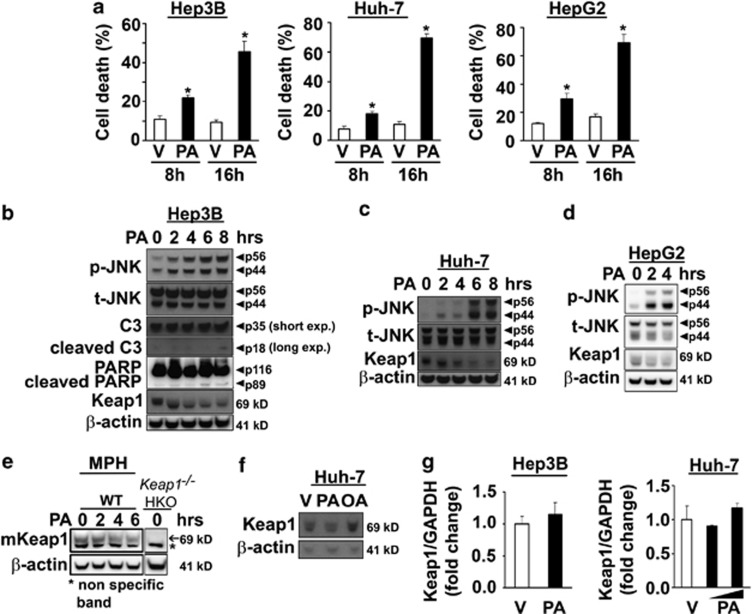
Figure 1.
PA-induced toxicity correlates with cellular Keap1 protein degradation and JNK activation in liver cells. (a) Cell death was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay in Hep3B, Huh-7 and HepG2 cells treated for 8 and 16 h with PA. The concentration of PA was 400 μM for Hep3B and HepG2 cells and 600 μM for Huh-7 cells. Vehicle (V)-treated cells were used as control. Data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. for three experiments; *P<0.05. B-E, (b) Hep3B, (c) Huh-7, (d) HepG2 cells and (e) primary murine hepatocytes isolated from WT mice were incubated with PA at the indicated time points. The concentration of PA was 400 μM for Hep3B and HepG2 cells and 600 μM for Huh-7 cells and primary hepatocytes. Lysates from untreated hepatocyte specific Keap1 knockout (Keap1−/− HKO) primary mouse hepatocytes were used as a control for the specificity of Keap1 antibody (e). Whole-cell lysates were prepared and immunoblot analysis were performed for phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), total JNK (t-JNK), caspase-3 (C3) displaying cleaved caspase-3 product p18, PARP displaying cleaved PARP product p89 and Keap1. The cleaved form of C3 was only visualized after long exposure times. β-Actin was used as a control for protein loading. (f) Whole-cell lysates were obtained from Huh-7 cells treated for 6 h with either PA (400 μM) or oleate (OA, 400 μM), and immunoblot analysis were performed for Keap1 and β-actin, a control for protein loading. (g) Total RNA was extracted from Hep3B and Huh-7 cells 6 h after treatment with PA, and vehicle (V) was used as control. The concentration of PA was 400 μM for Hep3B and 400 μM or 600 μM for Huh-7 cells. Fold induction was determined after normalization to GAPDH. Data represent the mean and error of three independent experiments