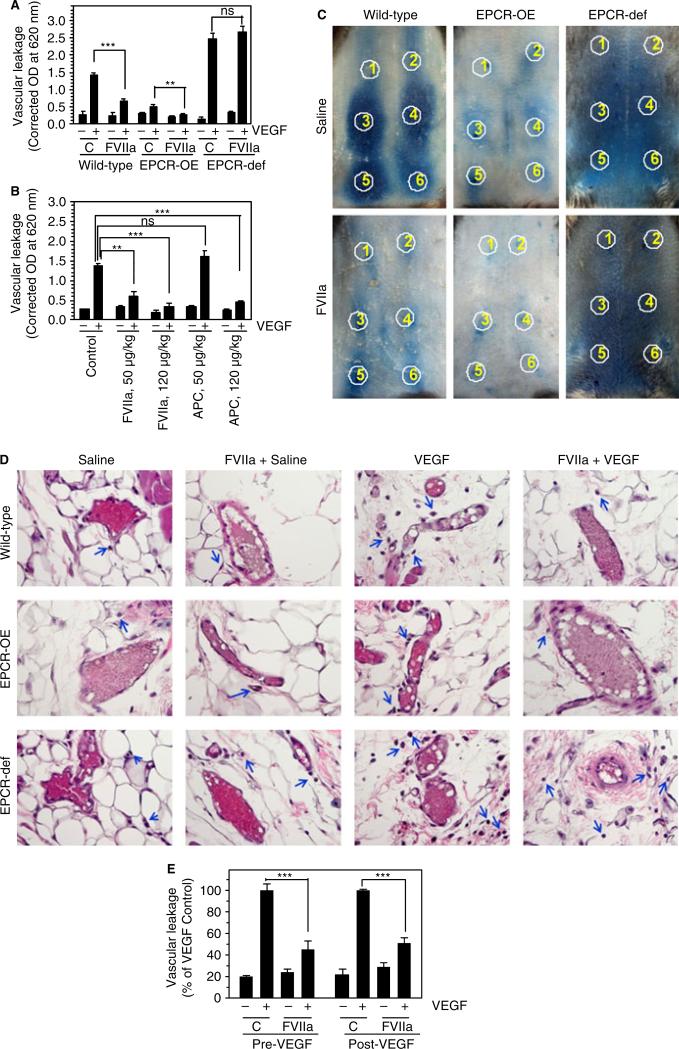
Fig. 3.
FVIIa suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced vascular permeability requires endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). (A) Wild-type EPCR-overexpressing (EPCR-OE) or EPCR-deficient (EPCR-def) mice were injected with saline or FVIIa (400 μg kg−1 body weight), followed by Evans blue dye (1%, 100 μL), intravenously via the tail vein. After 30 min, saline or VEGF (50 ng) was injected intradermally at six different sites (two with saline, and four with VEGF). Thirty minutes after injection of VEGF, dermal tissues around the injection sites were removed by biopsy, the dye in the skin biopsies was eluted, and the absorbance of the dye was measured as described in Materials and methods (five mice per group). (B) Wild-type mice were injected with saline or varying doses of FVIIa or activated protein C (APC) (50 or 120 μg kg−1), followed by Evans blue dye, and VEGF was then injected intradermally, as described in (A) (six mice per group). (C) Wild-type EPCR-OE or EPCR-def mice were injected with saline or FVIIa (120 μg kg−1 body weight), followed by Evans blue dye, and VEGF was then injected intradermally. Photographs were taken 30 min after VEGF administration. Circles indicate injection sites; 1 and 2 indicate saline-injected sites, and 3–6 indicate VEGF-injected sites. The photographs shown are representative of five mice per group. (D) Histological examination of skin tissue sections of wild-type, EPCR-OE and EPCR-def mice injected with saline or FVIIa (120 μg kg−1 body weight), and then intradermally injected with saline or VEGF. The blue arrows indicate extravasated leukocytes. The images shown in the figure are representative micrographs from > 20 images obtained from skin tissue sections by two different investigators (six mice per group). (E) Wild-type mice were first injected with saline or FVIIa (120 μg kg−1), and then with Evans blue dye via the tail vein, and saline or VEGF intradermally (Pre-VEGF). In the Post-VEGF group, wild-type mice were first injected intradermally with saline or VEGF, and 30 min later, FVIIa (120 μg kg−1) or saline was given intravenously. Thirty minutes after FVIIa administration, Evans blue dye was injected into the mice. Leakage of the dye into skin tissues was measured 30 min after VEGF (Pre-VEGF) or Evans blue dye (Post-VEGF) administration (six mice per group). Values were normalized to the value obtained in the VEGF-injected mice that were not treated with FVIIa within the specific experimental group. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. C, control; NS, no statistically significant difference.