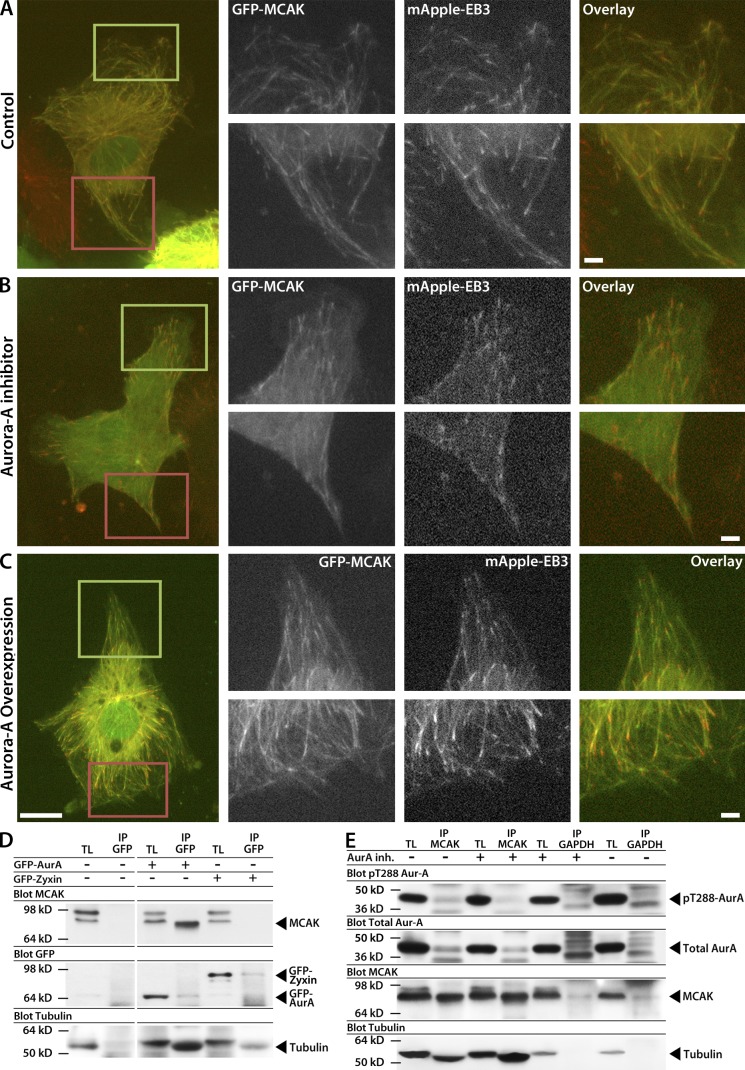
Figure 4.
Aurora A activity is required for association with MCAK but does not affect MCAK localization to growing MT plus ends. (A–C) Images showing the whole cell (left) and zoomed regions of the leading (green boxes and top right row) and trailing edges (red boxes and bottom right row) of HUVECs at the edge of a monolayer wound coexpressing mApple-EB3 and low levels of GFP-MCAK. The wound edge faces up. Fluorescent images reveal MCAK localization to growing MT plus ends in HUVECs in untreated control (A), treated with 40 nM Aurora A inhibitor (B), or overexpressing Aurora A (C). (D) Immunoprecipitation from HUVEC lysates with anti-GFP antibodies in HUVECs in the absence (−) or presence (+) of GFP–Aurora A or GFP-Zyxin expression and Western blot with anti-MCAK (top) or anti-GFP antibodies (bottom). Note that MCAK appears as a doublet in HUVEC lysates, and that the lower molecular mass form exclusively coimmunoprecipitates with Aurora A. (E) Immunoprecipitation with anti-MCAK or anti-GAPDH antibodies from HUVEC cell lysates prepared in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 40 nM Aurora A inhibitor and Western blot with anti–pT288–Aurora A, anti–Aurora A, and anti-MCAK antibodies. Western blot for tubulin shows coprecipitation with GFP–Aurora A (D) and with MCAK (E). IP, immunoprecipitate; TL, total lysate. Bars: (main) 10 µm; (zoomed) 2 µm.