Figure 5.
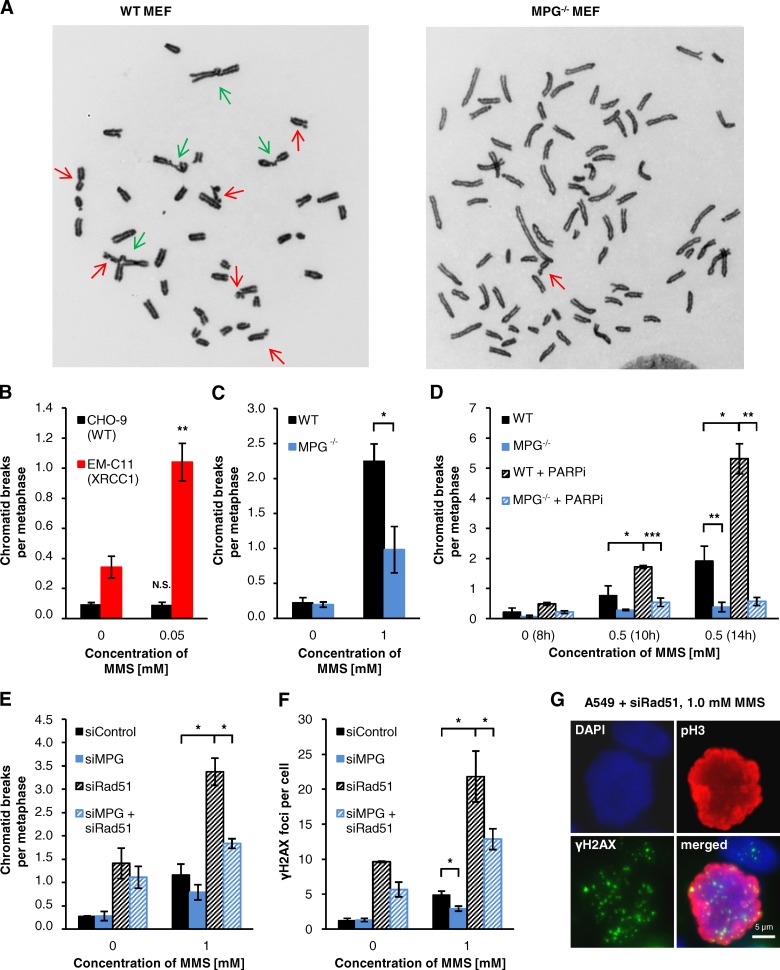
DSBs formed after MMS at BER intermediates cause chromatid breaks. (A) Representative images of MMS-induced chromosomal aberrations in PARPi-treated WT and MPG−/− MEFs (14 h after 0.5 mM MMS). Chromatid breaks and chromatid-type translocations are marked by red and green arrows, respectively. Chromatid breaks were analyzed in (B) CHO-9 (WT) and EM-C11 (XRCC1-deficient) cells, (C and D) WT and MPG−/− MEFs with or without PARPi, and (E) siRNA-treated A549 cells. Data in B, C, and E were obtained from the experiments performed for Fig. 4, B, C, and D. For D, 15 µM PARPi was added 1 h before MMS and was only present until the end of the MMS treatment. Therefore, PARPi had only an impact on cells in S phase. The analysis times for D (6–8 h for untreated cells and 8–10 h or 12–14 h for MMS-treated cells) were chosen such that cells in S phase at the time of MMS treatment had progressed into mitosis. (F and G) γH2AX foci in mitotic A549 cells after siRNA for 72 h. Cells were treated with 1 mM MMS for 1 h and caffeine was added at 20 h after MMS. 2 h later, samples were fixed and stained against γH2AX and pH3. γH2AX foci were assessed in mitotic cells (F); a representative image for foci in mitotic cells is shown in G (±SEM from 3–5 experiments). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.