Figure 1.
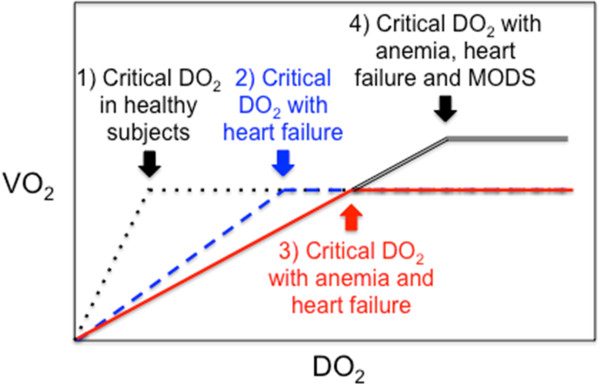
Critical oxygen delivery (DO2), cardiac failure, anemia and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). X axis:systemic DO2; Y axis: global oxygen consumption (VO2). Critical DO2: level below which DO2 does not meet oxygen demand (O2 supply dependency). (1) In healthy subjects (dotted black and white line), as DO2 decreases, VO2 remains constant by compensatory mechanisms (increased cardiac output and cellular O2 extraction). (2) Cardiac failure limits compensatory increase in cardiac output (hatched blueline). (3) This limitation is worst in patients with anemia and heart failure (plain red line) because low hemoglobin decreases arterial oxygen content (CaO2). (4) Severe cardiac dysfunction may be associated with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), both of which increase systemic VO2 and therefore critical DO2 (double black line).
