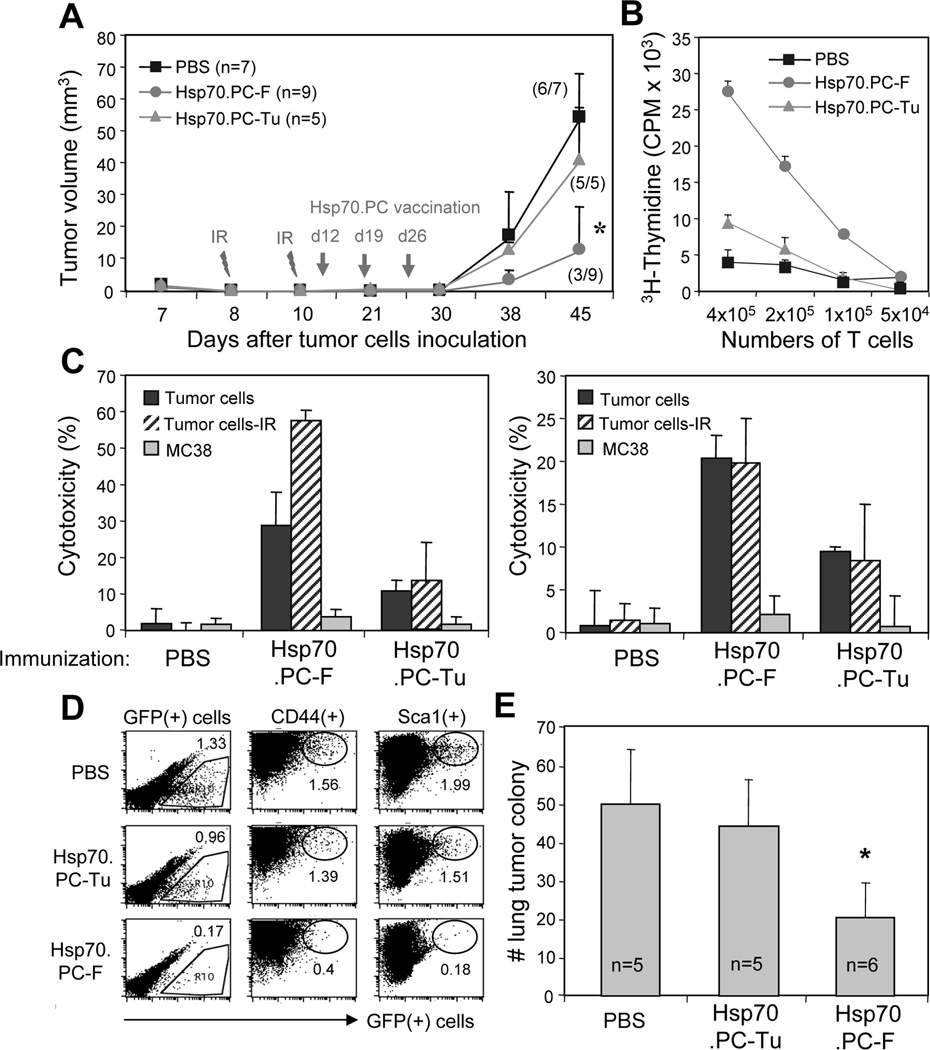
FIGURE 5.
Combined radiotherapy and immunotherapy in the treatment of mammary tumors with early metastasis. (A) Naïve mice were inoculated with 1×106 of GFP+MMT tumor cells in the mammary fat pad. The tumor were irradiated on days 8 and 10 by X-RAD 320 X-Ray Biological Irradiator (XRAD 320, Precision x-ray, Inc.). The mice were then randomly divided into 3 groups and immunized with 10 µg Hsp70.PC-F or Hsp70.PC-Tu. Mice injected with PBS were used as control. The tumors were measured for up to 45 days and tumor volume and tumor incidence was presented (A). The statistical significance was determined by One-way ANOVA. (*) indicates P<0.001). (B) T cells proliferation. (C) CTL activity against ionizing radiation (IR) selected, unselected tumor or unrelated tumor cells (MC38) at 100:1 of E: T ratios were measured. CTL activity of LNC (left panel) or splenocytes (right panel) against indicated targets was determined by 51Cr-release assay. (D) The lungs collected from individual mouse were carefully perfused to remove circulating cells before being processed to determine the GFP+ tumor cells by FACS. The percentage of GFP+ disseminated cells in total lung cells was indicated for each group. (E) The numbers of tumor cell colonies from the lungs of recipient mice were counted and presented. The statistical significance was determined by One-way ANOVA. (*) indicates P<0.001.