Figure 7.
Impact on the Catalytic Properties of PPIP5K2KD Following Mutation of K54, K103, E192, and K213
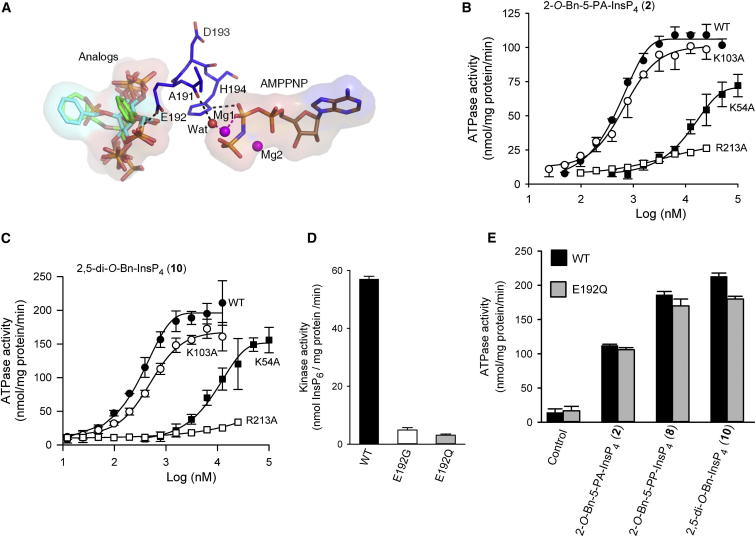
(A) The spatial separation of AMPPNP from the PPIP5K2KD substrate capture site. Protein residues are shown as stick models. AMPPNP, and inositol phosphate analogs 5-PA-InsP5 (1), 2-O-Bn-5-PA-InsP4 (2), and 2,5-di-O-Bn-InsP4 (10) and all are shown as stick models. Atoms are blue for nitrogen; red for oxygen; orange for phosphorus; and gray, cyan, or green for carbon. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines.
(B and C) Dose-response curves for the effects of 2-O-Bn-5-PA-InsP4 (2) and 2,5-di-O-Bn-InsP4 (10) upon the ATPase activities of wild-type PPIP5K2KD (closed circles; data are taken from Figure 2A) and the following mutants: K54A mutant (closed squares), K103A (open circles), and R213A (open squares).
(D) The InsP6 kinase activities of wild-type, E192G, and E192Q mutants of PPIP5K2KD, determined with 5 μM substrate.
(E) The ATPase activities of wild-type and E192Q mutants of PPIP5K2KD obtained in the presence of the indicated analogs, at concentrations of 25 μM. Error bars represent SEs from three experiments (error bars are not shown when they are smaller than the symbol).