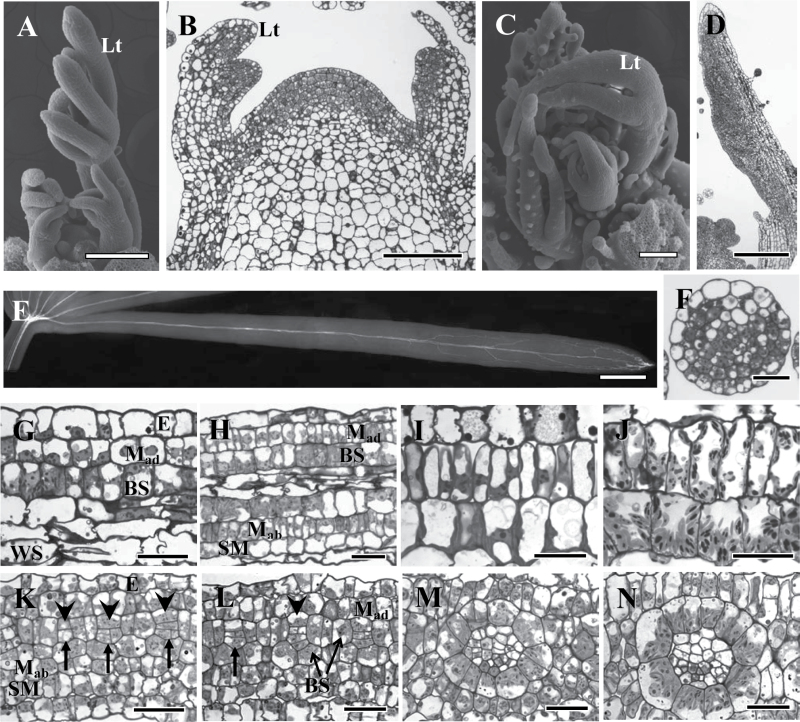
Fig. 1.
Vegetative shoot tip structure and early stages of leaf development in two Cleome species, C. angustifolia (A, B, E–J) and C. gynandra (C, D, K–N). (A, C) Scanning electron microscopy of shoot tips. (B, D) Light microscopy of longitudinal sections of the shoot apical meristem showing initiation and development of the leaflet. (E) Cleared young leaflet of C. angustifolia under UV light showing the basipetal direction of lateral vein development. (F) Cross-section of the young (0.5mm) C. angustifolia leaf. (G–J) Longitudinal sections showing the formation of cell lineages from the base of young leaves (G) to the tip (J), with the direction of maturation from left to right in C. angustifolia. The adaxial double-layered chlorenchyma (M and BS) differentiation is shown at Stages 1 (G), 2 (H, note the abaxial SM delimited), 3 (I), and 4 (J). (K–N) Procambial strand initiation and Kranz anatomy development around the veins from the base of young leaves (K) to the tip (N), with the direction of maturation from left to right in C. gynandra. (K) Procambium initials are indicated by arrows; arrowheads show the first adaxial BS cell progenitor; note the additional abaxial SM layer formed. (L) BS progenitors derived from second and third ground meristem layers are indicated. Different stages of M and BS differentiation are shown for C. gynandra: Stage 1 (L), 2 (M), and 3 (N). E, epidermis; BS, bundle sheath; Lt, leaflet; Mad, adaxial mesophyll; Mab, abaxial mesophyll; SM, spongy mesophyll; WS, water storage. Scale bars=200 μm for A, C, D; 100 μm for B; 0.5mm for E; 20 μm for F–N.