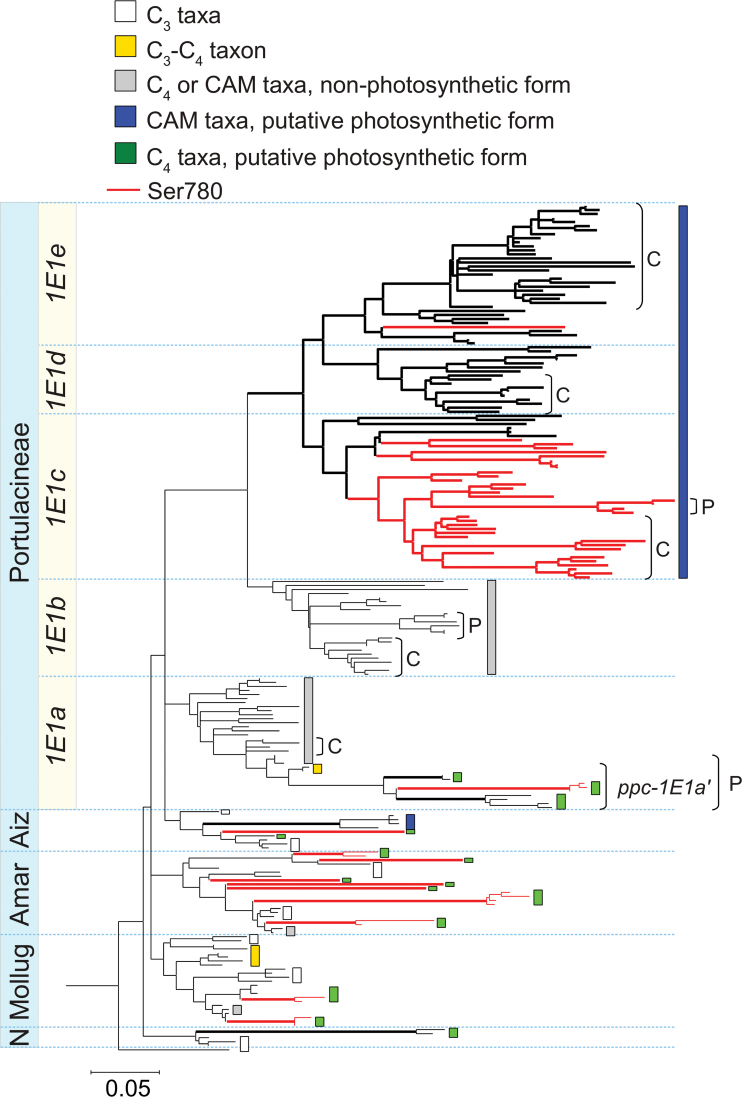
Fig. 3.
Evolution of ppc-1E1 in Caryophyllales. The topology was inferred on nucleotide sequences, but branch lengths were estimated based on amino acid sequences. The branch lengths inferred on nucleotide sequences, together with all species names and support values, are available in Fig. S1. Groups of genes encoding a Ser780 are highlighted by red branches. Branches where some sites underwent an excess of non-synonymous mutations according to the best model are thicker. Putative C4 forms are delimited in green and putative CAM forms in blue. These were identified based either on transcript abundances in specific conditions, on the literature, or on an excess of amino acid changes in C4/CAM species. Genes of C4 or CAM taxa that represent putative non-photosynthetic duplicates are delimited in grey, those of C3 taxa in white, and those of C3–C4 taxa in yellow. Families outside Portulacineae and gene lineages for Portulacineae are indicated on the left: N, Nyctaginaceae; Mollug, Molluginaceae; Amar, Amaranthaceae; Aiz, Aizoaceae. Subclades of interest are indicated on the right: P, Portulaca; C, cacti. The full phylogenetic tree is available in Fig. S3. The scale bar represents expected substitutions per site. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)