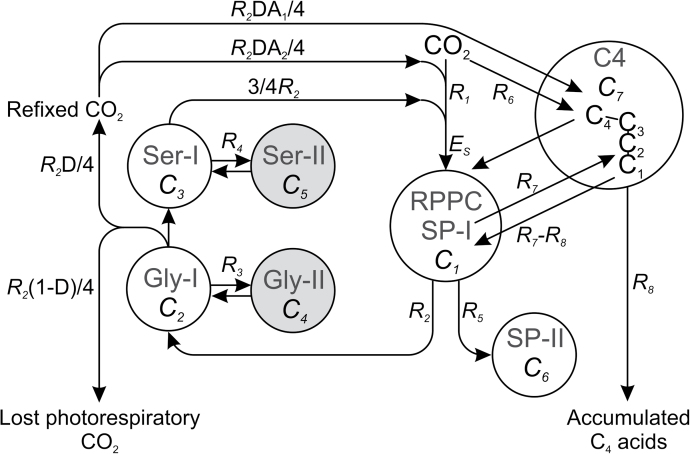
Fig. 1.
Model of major photosynthetic-photorespiratory carbon fluxes in Flaveria including the reductive pentose phosphate cycle (RPPC) with the attached photorespiratory pathway and the C4 photosynthetic pathway. R 1, rate of CO2 fixation in RPPC; R 2, rate of carbon flux through the glycolate cycle; R 3, rate of carbon exchange between different pools of glycine; R 4, rate of carbon exchange between different pools of serine; R 5, rate of transport of sugar phosphates out of the RPPC; R 6, rate of CO2 fixation by the C4 pathway; R 7, rate of carbon flux from RPPC into ‘C3 skeletons’ of C4 acids, R 8, rate of accumulation of C4 acids; C 1, total pool of sugar phosphates in the RPPC; C 2, active pool of the glycine branch of the photorespiratory pathway; C 3, active pool of the serine branch of the photorespiratory pathway; C 4 and C 5, corresponding non-photorespiratory metabolite pools; C 6, extra-cyclic pool of sugar phosphates; C 7, total pool of C4 acids. D (reassimilation coefficient) describes the fraction of refixed relative to total photorespiratory CO2. A 1 and A 2 are the partition coefficients describing the relative contributions of the RPPC and the C4 pathway to refixation of photorespiratory CO2. Note that Gly-I and Ser-I also include all other metabolites from the respective branches of the photorespiratory pathway. Gly-II and Ser-II represent less mobile (cytosolic, plastidial, vacuolar) pools of these metabolites.