Abstract
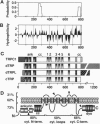
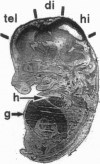
In many vertebrate and invertebrate cells, inositol 1,4,5-trisphospate production induces a biphasic Ca2+ signal. Mobilization of Ca2+ from internal stores drives the initial burst. The second phase, referred to as store-operated Ca2+ entry (formerly capacitative Ca2+ entry), occurs when depletion of intracellular Ca2+ pools activates a non-voltage-sensitive plasma membrane Ca2+ conductance. Despite the prevalence of store-operated Ca2+ entry, no vertebrate channel responsible for store-operated Ca2+ entry has been reported. trp (transient receptor potential), a Drosophila gene required in phototransduction, encodes the only known candidate for such a channel throughout phylogeny. In this report, we describe the molecular characterization of a human homolog of trp, TRPC1. TRPC1 (transient receptor potential channel-related protein 1) was 40% identical to Drosophila TRP over most of the protein and lacked the charged residues in the S4 transmembrane region proposed to be required for the voltage sensor in many voltage-gated ion channels. TRPC1 was expressed at the highest levels in the fetal brain and in the adult heart, brain, testis, and ovaries. Evidence is also presented that TRPC1 represents the archetype of a family of related human proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Ankyrins. Adaptors between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8703–8706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Calcium oscillations. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9583–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. S., Rossier M. F., Hughes A. R., Shears S. B., Armstrong D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of Ca2+ entry into acinar cells by a non-phosphorylatable inositol trisphosphate. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):162–165. doi: 10.1038/352162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P. Hundreds of ankyrin-like repeats in functionally diverse proteins: mobile modules that cross phyla horizontally? Proteins. 1993 Dec;17(4):363–374. doi: 10.1002/prot.340170405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Jin H., Iida N., Brandt N. R., Zhang S. H. The involvement of ankyrin in the regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-mediated internal Ca2+ release from Ca2+ storage vesicles in mouse T-lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7290–7297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham D. E. Calcium signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham D. E. Intracellular calcium. Replenishing the stores. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):634–635. doi: 10.1038/375634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosens D. J., Manning A. Abnormal electroretinogram from a Drosophila mutant. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):285–287. doi: 10.1038/224285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Innocenti B., Pozzan T. Receptor-activated Ca2+ influx: how many mechanisms for how many channels? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Mar;15(3):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C., Minke B. Novel Ca2+ channels underlying transduction in Drosophila photoreceptors: implications for phosphoinositide-mediated Ca2+ mobilization. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Sep;16(9):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C., Minke B. The trp gene is essential for a light-activated Ca2+ channel in Drosophila photoreceptors. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90086-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harteneck C., Obukhov A. G., Zobel A., Kalkbrenner F., Schultz G. The Drosophila cation channel trpl expressed in insect Sf9 cells is stimulated by agonists of G-protein-coupled receptors. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 30;358(3):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01455-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Fasolato C., Penner R. Ion channels and calcium signaling in mast cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Dec 20;707:198–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb38053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):353–356. doi: 10.1038/355353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y., Schilling W. P. Receptor-mediated activation of recombinant Trpl expressed in Sf9 insect cells. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 15;305(Pt 2):605–611. doi: 10.1042/bj3050605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y., Vaca L., Zhu X., Birnbaumer L., Kunze D. L., Schilling W. P. Appearance of a novel Ca2+ influx pathway in Sf9 insect cells following expression of the transient receptor potential-like (trpl) protein of Drosophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jun 15;201(2):1050–1056. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Tracing the roots of ion channels. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):715–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90280-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Samanta S. Detergent solubility of the inositol trisphosphate receptor in rat brain membranes. Evidence for association of the receptor with ankyrin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6477–6486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyford G. L., Yamagata K., Kaufmann W. E., Barnes C. A., Sanders L. K., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Lanahan A. A., Worley P. F. Arc, a growth factor and activity-regulated gene, encodes a novel cytoskeleton-associated protein that is enriched in neuronal dendrites. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Clapham D. E. Calcium channels activated by depletion of internal calcium stores in A431 cells. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80467-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R. Pore loops: an emerging theme in ion channel structure. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):889–892. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Modular organization of actin crosslinking proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombie W. R., Heiner C., Kelley J. M., Fitzgerald M. G., Gocayne J. D. Rapid and reliable fluorescent cycle sequencing of double-stranded templates. DNA Seq. 1992;2(5):289–296. doi: 10.3109/10425179209030961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Jones K., Hafen E., Rubin G. Rescue of the Drosophila phototransduction mutation trp by germline transformation. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1040–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.3933112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila trp locus: a putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1313–1323. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Fasolato C., Hoth M. Calcium influx and its control by calcium release. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90130-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz A., Sandler C., Kirschfeld K., Hardie R. C., Minke B. Genetic dissection of light-induced Ca2+ influx into Drosophila photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Dec;104(6):1057–1077. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.6.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz A., Suss-Toby E., Rom-Glas A., Arnon A., Payne R., Minke B. The light response of Drosophila photoreceptors is accompanied by an increase in cellular calcium: effects of specific mutations. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1257–1267. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. M., Bull A., Kelly L. E. Identification of a Drosophila gene encoding a calmodulin-binding protein with homology to the trp phototransduction gene. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90085-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. A., Assaf A., Peretz A., Nichols C. D., Mojet M. H., Hardie R. C., Minke B. TRP, a protein essential for inositide-mediated Ca2+ influx is localized adjacent to the calcium stores in Drosophila photoreceptors. J Neurosci. 1995 May;15(5 Pt 2):3747–3760. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03747.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Bird G. S. The signal for capacitative calcium entry. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80061-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Capacitative calcium entry revisited. Cell Calcium. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(10):611–624. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90016-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Excitement about calcium signaling in inexcitable cells. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):676–678. doi: 10.1126/science.8235587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Blakemore K. J., Kearns W. G., Giraldez R. A., Escallon C. S., Pearson P. L., Stetten G. Analysis of reciprocal translocations by chromosome painting: applications and limitations of the technique. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):700–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaca L., Sinkins W. G., Hu Y., Kunze D. L., Schilling W. P. Activation of recombinant trp by thapsigargin in Sf9 insect cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 1):C1501–C1505. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.5.C1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong F., Schaefer E. L., Roop B. C., LaMendola J. N., Johnson-Seaton D., Shao D. Proper function of the Drosophila trp gene product during pupal development is important for normal visual transduction in the adult. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]