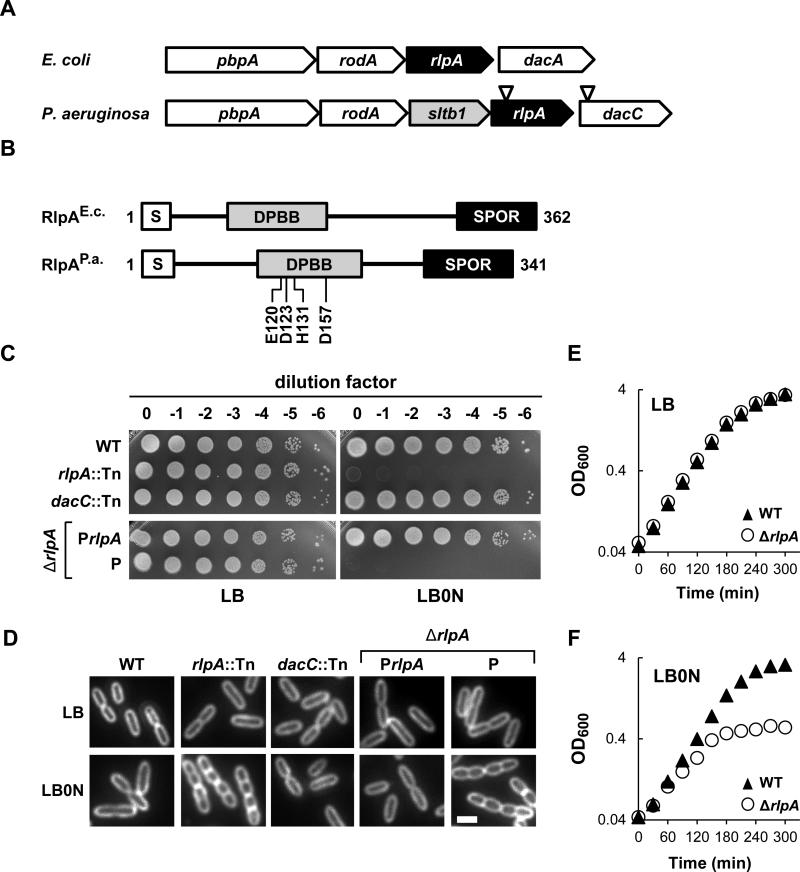
Figure 2. Growth and chaining of an rlpA mutant.
(A) rlpA loci from E. coli K-12 and P. aeruginosa UCBPP-PA14. Inverted triangles depict relative positions of the MAR2xT7 transposon in rlpA and dacC. PBPA is a transpeptidase needed for cross-linking PG, especially during elongation. RodA is considered to be a flippase that transports lipid-linked disaccharide-pentapeptide precursors to the periplasm for PG synthesis during elongation. DacA is a PG carboxypeptidase. SltB1 is a soluble lytic transglycosylase found in the periplasm. DacC is a PG carboxypeptidase more closely related to DacC of E. coli than to DacA of E. coli. (B) Schematic diagram of the domain architecture of RlpA. S, type II signal sequence. DPBB, RlpA-like double psi beta barrel domain. SPOR, SPOR domain. DPBB domain residues targeted for mutagenesis are shown below the P. aeruginosa protein. (C) Plating efficiency. Tenfold serial dilutions of cells with the indicated genotypes were spotted onto LB (left) or LB0N (right). Plates were photographed after incubation overnight at 37°C. P refers to the empty vector (pJN105), while PrlpA refers to a derivative (pDSW1398) that carries rlpA. (D) Division phenotypes. Cells grown at 37°C in LB or LB0N to an OD600 ~0.5 were fixed, stained with the membrane dye FM4-64 and photographed under fluorescence. The white bar represents 2 μm. (D) Growth curves for wild type and the ΔrlpA mutant grown in LB or LB0N at 37°C. Strains shown are MJ1 (WT), MJ7 (rlpA::Tn), MJ18 (dacC::Tn), MJ27 (ΔrlpA/PrlpA), MJ26 (ΔrlpA/P) and MJ24 (ΔrlpA).