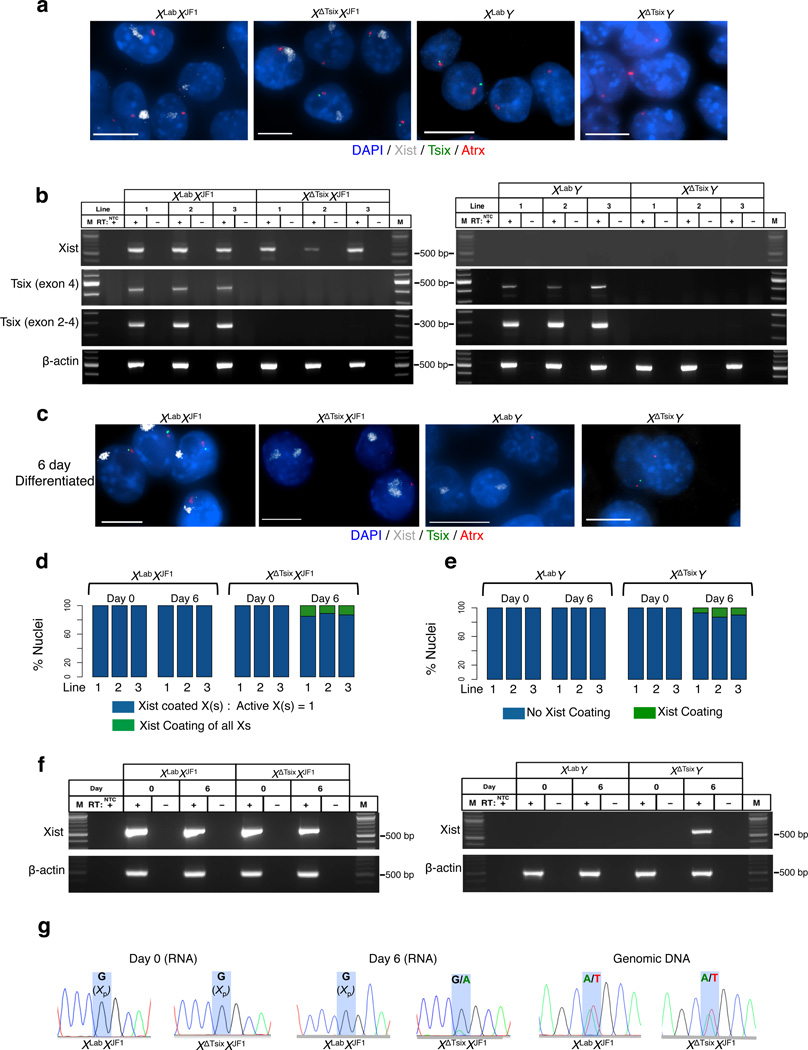
Figure 3. The XΔTsix maternal X-chromosome displays ectopic Xist induction only upon differentiation in trophoblast stem (TS) cells.
RNA FISH detection of Xist (white), Tsix (green), and Atrx (red) RNAs in representative TS cell lines. Nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 µm. Three cell lines of each genotype were analyzed. (b) RT-PCR detection of Xist, Tsix (two different amplicons), and control b-actin RNAs in wild-type (WT) and Tsix-mutant TS cells. Three TS cell lines of each genotype were analyzed. M, marker; NTC, no template control; +, RT; -, no RT control lane. (c) RNA FISH detection of Xist (white), Tsix (green), and Atrx (red) RNAs in 6-day (d6) differentiated TS cell lines. Three cell lines of each genotype were analyzed. Scale bar, 10 µm. (d) Quantification of Xist induction from the XΔTsix X-chromosome in females. Aberrant Xist RNA coating (defined as two Xist RNA coats in a diploid cell or Xist coating of all chromosomes in polyploid giant cells) is observed in mutant but not WT d6 differentiated TS cells. For giant cells, the number of X-chromosomes was identified based on distinct Xist and Atrx RNA FISH signals. n=100 nuclei counted for each cell line per day of differentiation. (e) Quantification of Xist induction from the XΔTsix X-chromosome in males. Aberrant Xist RNA coating is observed in mutant but not WT d6 differentiated TS cells. n=100 nuclei counted for each cell line per day of differentiation. (f) RT-PCR detection of Xist and control b-actin RNA in undifferentiated (d0) and d6 differentiated wild-type (WT) and Tsix-mutant TS cells. A single representative TS cell line from each genotype is shown. M, marker; NTC, no template control; +, RT; -, no RT control lane. (g) Sanger sequencing chromatograms of representative XLabXJF1 and XΔTsixXJF1 Xist RT-PCR products (RNA), and an Xist genomic DNA amplicon (gDNA) within exon 1. Highlights mark a single nucleotide polymorphism that differs between the maternal XLab / XΔTsix alleles and the paternal XJF1 Xist allele.