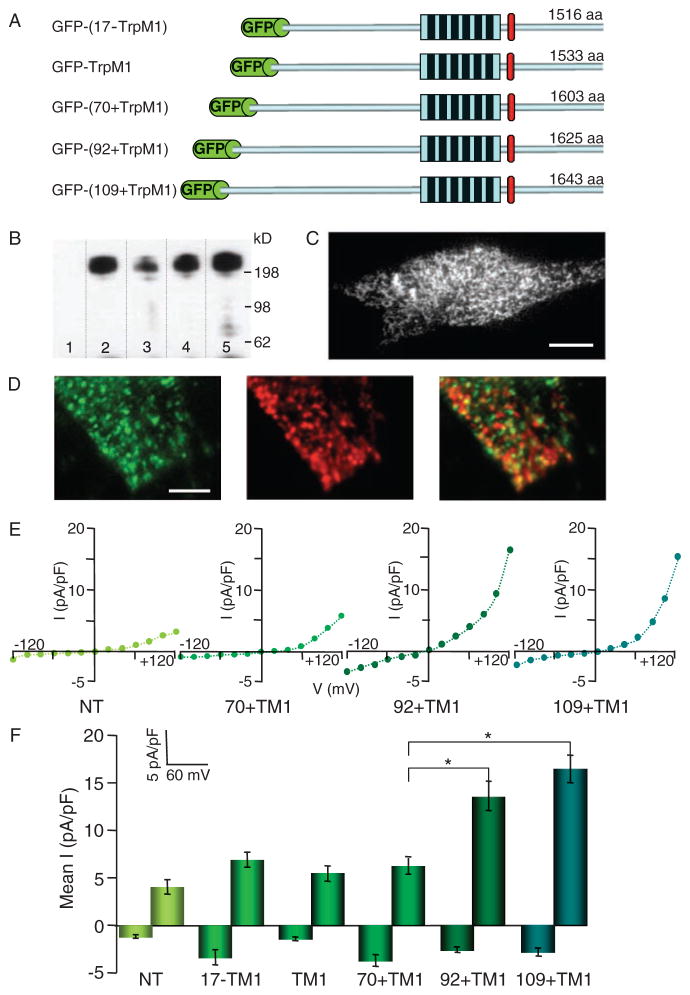
Fig. 3.
Expression of GFP-tagged TRPM1 in SK-Mel19 human melanoma. (A) Schematic representation of GFP-tagged TRPM1 ion channel isoforms. GFP is fused to the N termini of TRPM1 isoforms. All isoforms share the identical six transmembrane domains and residues thereafter to the end of the C termini. The TRPM1 isoforms have varying numbers of amino acids because of different lengths of their N termini. (B) Western blot of GFP-TRPM1 isoforms immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells using a polyclonal anti-GFP and probed with a monoclonal anti-GFP. Immunoblotting of GFP-(17−TRPM1) (lane 2), GFP-TRPM1 (lane 3), GFP-(70+TRPM1) (lane 4), and GFP-(92+TRPM1) (lane 5) results in a single band corresponding to the full-length protein that is absent in nontransfected cells (lane 1). (C) TIRF image of SK-Mel22a melanoma cells expressing GFP-TRPM1. GFP-TRPM1 is primarily localized to intra-cellular vesicular structures (Movie S1). Calibration bar, 5 μm. (D) TIRF image of a region of an SK-Mel19 cell expressing GFP-(92+TRPM1) and immunostained with anti-GFP (left) and anti-melanosomal marker (Pmel17) (middle). Overlay of the two images (right) shows no significant colocalization of GFP-TRPM1 and melanosomes. Calibration bar, 1.2 μm. (E) I-V curves from individual SK-Mel19 cells nontransfected (NT), expressing GFP-(70+TRPM1), GFP-(92+TRPM1), or GFP-(109+TRPM1). (F) Mean inward (−120 mV) and outward (+120 mV) current amplitudes recorded from nontransfected SK-Mel19 cells (NT, n = 5) and SK-Mel19 cells expressing GFP-(17−TRPM1) (n = 4), GFP-TRPM1 (n = 10), GFP-(70+TRPM1) (n = 8), GFP-(92+TRPM1) (n = 10), and GFP-(109+TRPM1) (n = 12). *P < 0.001; t test. Error bars, ± SEM.