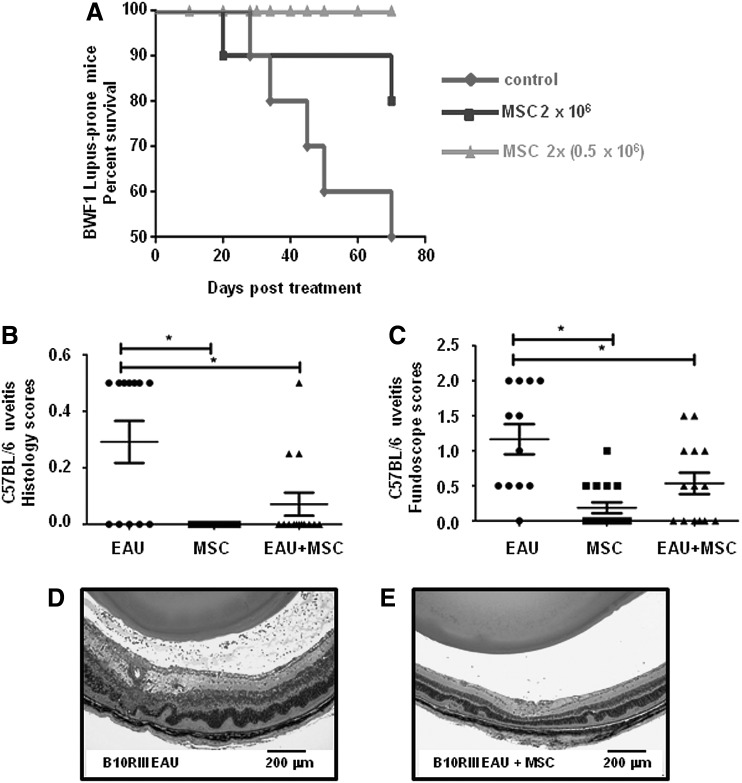
FIG. 6.
Proof of principle in vivo testing for hESC-MSC therapeutic activity in two autoimmune disease mouse models. (A) Kaplan–Meier plot showing the effects of hESC-MSCs on survival of lupus-prone BWF1 mice, n=10 per group. MSCs were intravenously injected as either a single bolus (black line with squares) or two injections, 2 weeks apart (gray line with triangles) when BWF1 mice were 24 weeks of age. Their survival was compared with untreated control BWF1 mice (black line with diamonds). BWF1 mice have a naturally reduced lifespan (50% median survival of ∼34–35 weeks, due to lupus nephritis and kidney dysfunction). (B, C) Histology scores and fundoscopic scores of eyes from C57BL/6 mice induced with mild uveitis [experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU), n=6], not induced with EAU but receiving hESC-MSCs on day 0 (MSC, n=8), and EAU-induced mice that also received a single injection of MSCs on day 0 (EAU+MSC, n=7). Scoring was performed at 21 days post-disease induction for both eyes from each mouse, by two independent investigators in a blinded fashion. A standard 0–4 scale was used to score severity with the higher the score indicating a more severe phenotype. (D, E) Pilot study of severe EAU induced in B10RIII mice (n=2 per group). Images are histology sections of eyes from EAU B10RIII mice that did not receive any MSCs (left panel, EAU) or EAU mice which did receive MSCs (right panel, EAU+MSC). Pronounced inflammatory cell infiltration and disruption of retinal architecture is noted in the image on the left, while less inflammatory signs are noted in the eyes of an MSC-treated animal shown on the right. Scale bar=200 μm. *Indicates P<0.05.