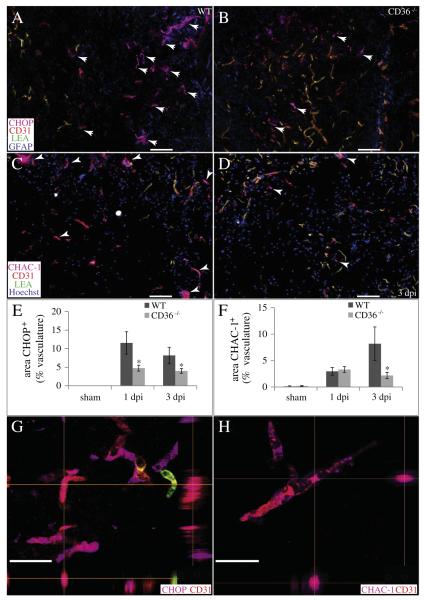
Fig. 8.
CD36 deletion decreases vascular ER stress responses and pro-apoptotic signaling following SCI. (A, B, E, G) The percentage of injury heterodomain CD31+ (red) microvessels which co-localize with the pro-apoptotic ERSR protein CHOP (pink) is significantly reduced in CD36−/− mice at 1 and 3 dpi. GFAP (blue) and LEA (green) are also shown. (C, D, F, H) The percentage of injury heterodomain CD31+ (red) microvessels which co-localize with pro-apoptotic CHAC-1 (pink) is significantly reduced in CD36−/− mice by 3 dpi. Hoechst (blue) and LEA (green) are also shown. Data are means ± SEM (WT, n = 4; CD36−/−, n = 4 per timepoint; *p < 0.05). Bars = 100 μm. Confocal imaging reveals co-localization of CHOP (G) or CHAC-1 (H) within the CD31+ microvasculature. XZ and YZ planes are indicated by the perpendicular orange lines. Bars = 25 μm.