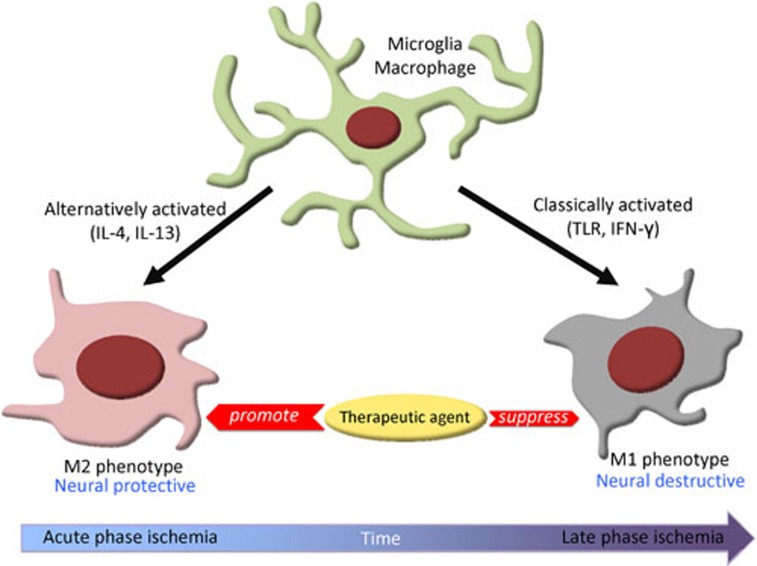
Figure 1.
Microglia/macrophages possess dual but opposite roles in the inflammatory responses progression in stroke. At early stage of hypoxic/anoxic condition, microglia/macrophages are mostly differentiated into the neuroprotective M2 phenotype. With time, microglia/macrophages gradually transform into a neuronal injurious M1 phenotype. M1 phenotype is “classically activated via toll-like receptors or interferon-γ”, whereas M2 phenotype is “alternatively activated by interleukin 4 or interleukin 13”. Future investigation identifying new therapeutic agents that promote macrophage differentiation into M2 phenotype and suppress transformation of macrophage into M1 phenotype would be valuable in treating post-ischemic stroke inflammation. (IL-4, interleukin 4; IL-13, interleukin 13; TLR, toll-like receptor; IFN-γ, interferon-γ)