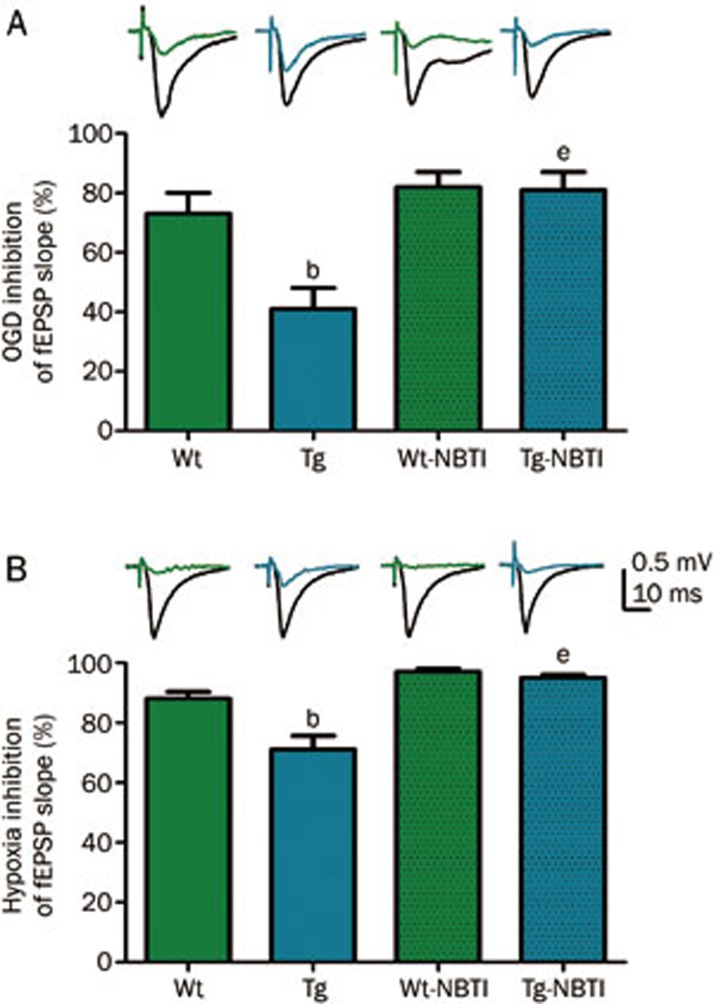
Figure 5.
Extracellular post-synaptic excitatory potentials (fEPSP) were recorded from electrically stimulated hippocampal slices from wild type (Wt) or hENT1 transgenic (Tg) mice. Synaptic responses were evoked by stimulation of the Schaffer collateral/commissural pathway with a concentric bipolar stimulating electrode with 0.1 ms pulse width at 30 s intervals. Extracellular field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) were recorded in striatum radiatum of CA1 hippocampus using glass microelectrodes (1–2 Ω) filled with aCSF. Slices were continuously superfused with aCSF or with 100 nmol/L S-(p-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine (NBTI) in aCSF at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min (32.5 °C). (A) Slices were exposed to glucose-free hypoxic aCSF (oxygen-glucose deprivation; OGD) for 3 min. (B) Slices were exposed to hypoxic aCSF for 10 min. Representative wave forms show fEPSP response before (black) or during OGD (A) or hypoxia (B) from Wt (green) or Tg (blue) slices. Bars are mean±SEM (n≥3) of maximally inhibited fEPSP responses, calculated as the difference between black and colored waveforms. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests. bP<0.05 vs Wt. eP<0.05 vs Tg. Data are adapted from24; for additional details on methods, see24.