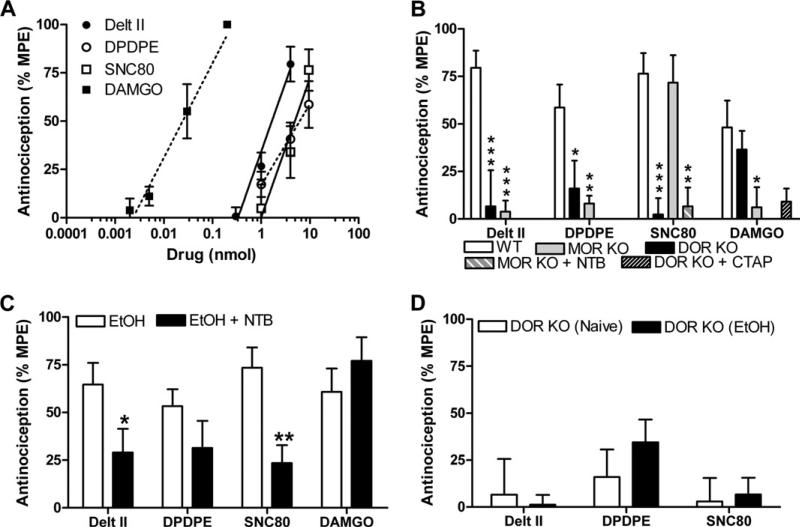
Figure 4.
Mechanical sensitivity is mediated by both delta opioid receptor (DOR) and mu opioid receptor (MOR) and is not altered by chronic ethanol exposure. (A) Wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice (n = 8–14) were injected intrathecally with increasing doses of a DOR-selective (deltorphin II, [D-Pen2,D-Pen5]-Enkephalin [DPDPE], or SNC80) or MOR-selective (DAMGO) agonist, and mechanical sensitivity was measured using von Frey filaments. (B) WT, DOR knockout (KO), and MOR KO C57BL/6 mice (n = 8–14) were injected intrathecally with agonist (deltorphin II [4 nmol], DPDPE [10 nmol], SNC80 [10 nmol], or DAMGO [30 pmol]), and mechanical sensitivity was measured. In WT mice, the DAMGO response was unaffected by co-injection of the DOR antagonist Naltriben (NTB) (.5 nmol). In MOR KO mice, the SNC80-induced response was inhibited by co-injection of the NTB (.5 nmol). Significance between groups was determined by analysis of variance followed by a Newman-Keuls post hoc analysis. (C) Ethanol-drinking WT, C57BL/6 mice (n = 8–14) were injected intrathecally with agonist (deltorphin II [4 nmol], DPDPE [10 nmol], SNC80 [10 nmol], or DAMGO [30 pmol]), and mechanical sensitivity was measured. Involvement DOR was determined by co-injection with the DOR-selective antagonist NTB (.5 nmol), respectively. (D) Naïve or ethanol-drinking C57BL/6 DOR KO mice (n = 8–9) were injected intrathecally with agonist (deltorphin II [4 nmol], DPDPE [10 nmol], or SNC80 [10 nmol]), and mechanical sensitivity was measured. Data are represented as the percentage maximal possible effect, which is defined as [(measurement – baseline)/(cutoff – baseline)]*100. *p < .05; **p < 0.01; ***p < .001. Delt II, deltorphin II; EtOH, ethanol; MPE, maximal possible effect.