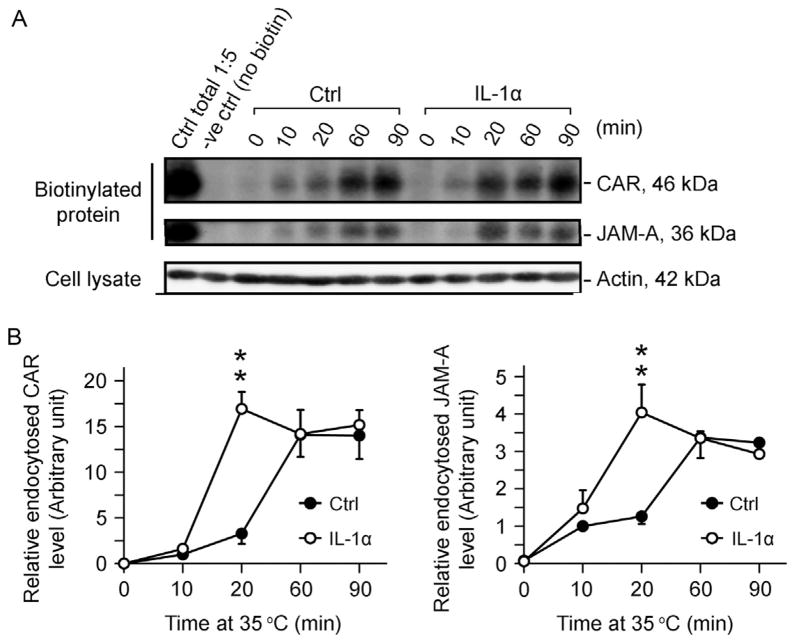
Figure 10.2.
Effects of IL-1α on the kinetics of endocytosis of CAR and JAM-A in Sertoli cells cultured in vitro with a functional tight junction-permeability barrier. Sertoli cells were cultured at 0.5 × 106 cells/cm2 for 4.5-day on Matrigel-coated dishes to allow the establishment of a functional TJ-permeability barrier. Thereafter, cells were subjected to biotinylation at 4 °C as described in text, and protein endocytosis was monitored at specified time points at 10, 20, 60, and 90 min versus time 0 in the absence (control, Ctrl) or presence of IL-1α (100 pg/ml) at 35 °C. (A) Endocytosed proteins at specified time points were monitored by extracting biotinylated proteins in cell lysates by using avidin-based resin for SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis after stripping of biotins from uninternalized biotinylated proteins on cell surface and quenching of the stripped free biotins in media. Following treatment of Sertoli cells with IL-1α which is known to perturb the Sertoli cell TJ-barrier function (Lie et al., 2011), an enhancement in endocytosis of CAR and JAM-A was noted. (B) Data were plotted against time to illustrate an increase in the kinetics of protein endocytosis following IL-1α treatment. Each data point is a mean ± SD of 3 replicates of a typical experiment, and this experiment was repeated three times using different batches of Sertoli cells. **P <0.01.