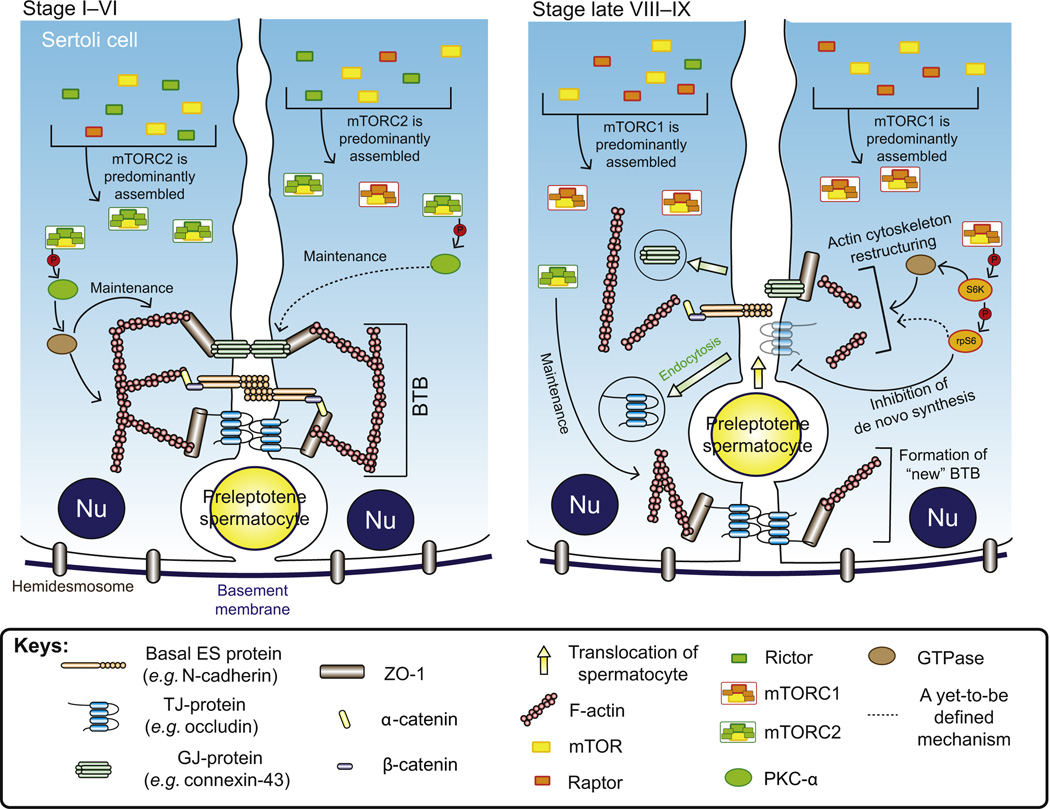
Figure 6.5. mTORC1 and mTORC2 display antagonistic effects on the BTB and their combined effects can protect the immunological barrier integrity during the transit of preleptotene spermatocytes at the BTB.
It is noted that rictor and raptor compete for mTOR for the formation of mTORC2 and mTORC1, respectively, to promote BTB and disrupt BTB integrity. At stages I–VI in which prior to BTB restructuring, the relative high expression of rictor favors the assembly of mTORC2, which is necessary for keeping the integrity of BTB by maintaining the dense F-actin network (namely the actin filament bundles at the basal ES), expression level of GJ proteins and GJ communication. On the other hand, in stage late VIII to stage IX that the BTB is transiently “open” to facilitate the transit of spermatocyte, the expression level of raptor is induced, whereas that of rictor is reduced. Thus, formation of mTORC2 is reduced and mTORC1 is favored. mTORC1 activates rpS6, which in turn disrupts the “old” BTB above the preleptotene spermatocytes in transit at the BTB by inhibiting de novo synthesis of BTB proteins. In addition, actin cytoskeleton reorganization during BTB restructuring is induced by (i) mTORC1 signaling via S6K1 and rpS6 and (ii) the decrease in phosphorylated PKC-α due to reduced mTORC2. The disorganized F-actin network leads to internalization of BTB proteins, which perturbs the “old” BTB. Furthermore, the decrease in GJ proteins and GJ communication caused by reduced mTORC2 also facilitates the disruption of the “old” BTB for the translocation of spermatocytes across the BTB. However, while mTORC2 expression is reduced, it remains to be robust enough to sustain the maintenance of the “new” BTB that is being assembled behind the preleptotene spermatocytes in transit. In short, utilizing the antagonistic effects of the mTORC1 and mTORC2 on the TJ-permeability barrier, the immunological barrier function can be maintained during the passage of preleptotene spermatocytes, which are connected in “clones” via intercellular bridges, at the BTB. For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the online version of this book.