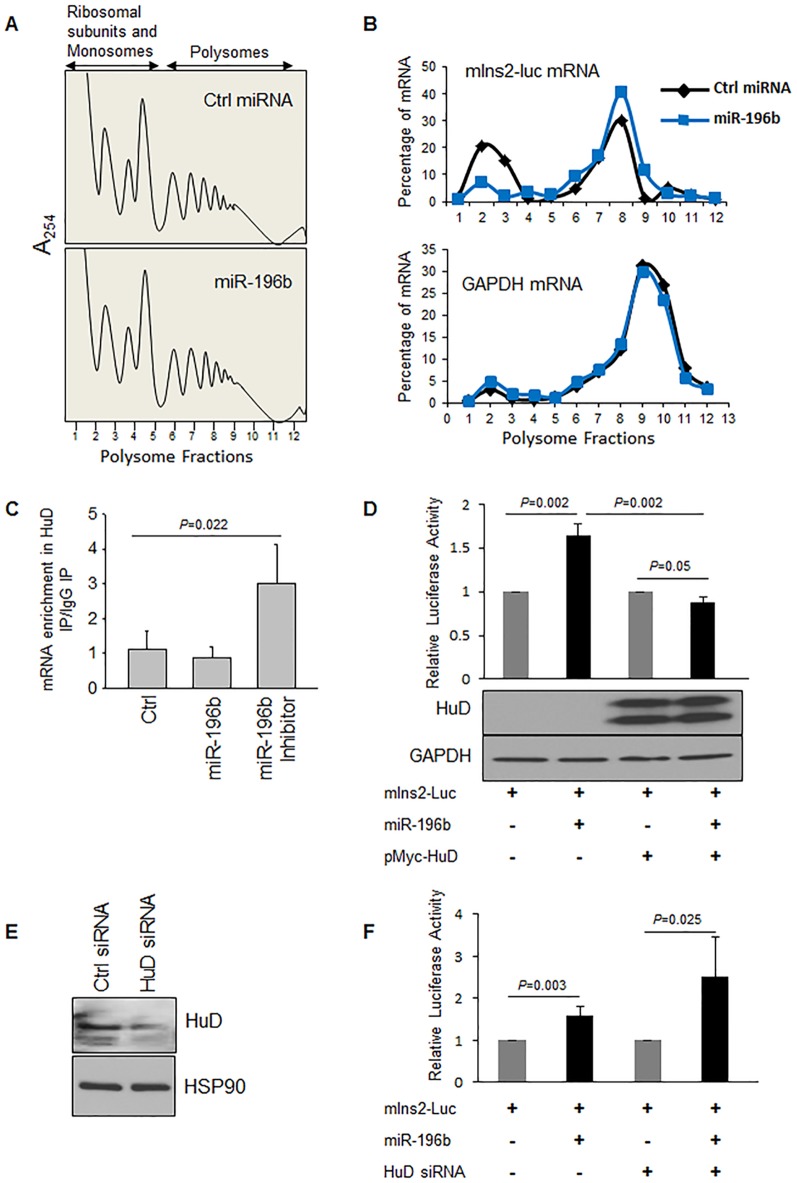
Figure 4. miR196b induces polysome association of Insulin2 reporter mRNA by inhibiting HuD binding.
(A) Lysates prepared from βTC6 cells transfected with Ctrl miRNA or mature miR-196 were fractionated through sucrose gradients to generate polysome profiles. Fractions 1–5 and 6–12 were considered as non-polysome and polysome respectively. (B) The relative distribution of Insulin2 reporter mRNA and GAPDH mRNA on polysome gradients was studied by RT-qPCR analysis of the RNA present in each of 12 gradient fractions, and represented as percentage of total mRNA. One of the representative experiments is shown here. (C) Interaction of HuD with Ins2-reporter mRNA in βTC6 cells transfected with control, mature miR-196b or miR-196b inhibitor, was studied by mRNP IP analysis using anti-HuD or control IgG antibodies. The RNA in the IP material was isolated, and Ins2-reporter mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR analysis and normalized to PGK mRNA levels. (D) Translation upregulation of insulin2 reporter with miR-196b in HEK293T cells transfected with either control or Myc-HuD plasmid. Lower panel shows the immunoblot for the over expression of Myc-HuD. (E, F) Forty-eight hours after transfection of βTC6 cells with Ctrl siRNA or HuD siRNA, HuD silencing was assessed by western blot analysis (E). Luciferase reporter with insulin2 5′UTR along with miR-196b or control miRNA duplex was introduced into βTC6 cells expressing normal or reduced HuD levels (F). The fold change in relative luciferase activity was measured with the activity of the luciferase construct with control miRNA set to 1. The graphs in (C,D,F) represent the means ± SD of 3-9 independent experiments; P values (Student's t-test) are indicated.