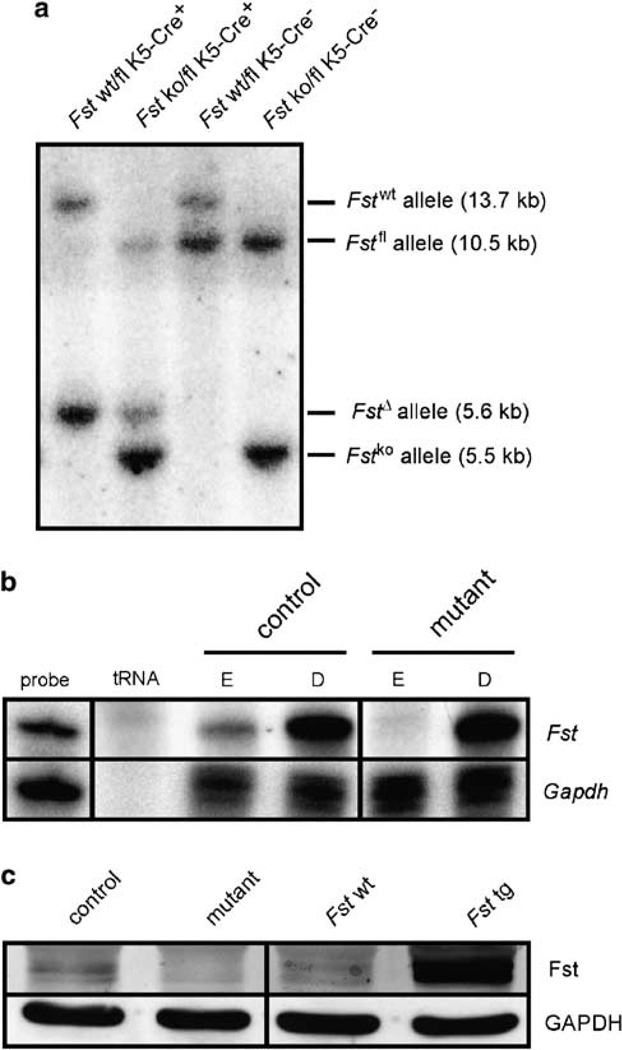
Figure 1.
Efficient knockout (ko) of follistatin in the epidermis. (a) Southern blot analysis showing Cre-mediated deletion of the floxed (fl) Fst allele. A 1230 bp SacI/HindIII probe was used to detect wild-type (wt), ko, fl and deleted (Δ) Fst alleles in genomic DNA digested with SacI and EcoRI.13 (b) Lack of follistatin mRNA in the epidermis is shown by RNase protection assay. Follistatin mRNA is expressed in the dermis and the epidermis of control mice but only in the dermis of Fst mutant mice. Samples of 20 µg of total RNA were used for hybridization. The hybridization probes (1000 c.p.m.) served as size markers (probe). tRNA (10 µg) was used as a negative control. Hybridization of RNA with a GAPDH riboprobe served as a loading control. (c) Western blot analysis showing lack of follistatin in primary keratinocytes isolated from mutant mice. Cell lysates were prepared from primary keratinocytes isolated from mutant (Fst ko/fl K5Cre+) and control (Fst wt/fl K5Cre−) littermates. Protein (100 µg) was analyzed by western blot analysis with an antibody against follistatin. Protein lysates of primary keratinocytes isolated from mice overexpressing follistatin in the epidermis (Fst tg)10 served as a positive control. Expression of follistatin in the wt littermates of these transgenic mice is also shown for comparison (Fst wt).