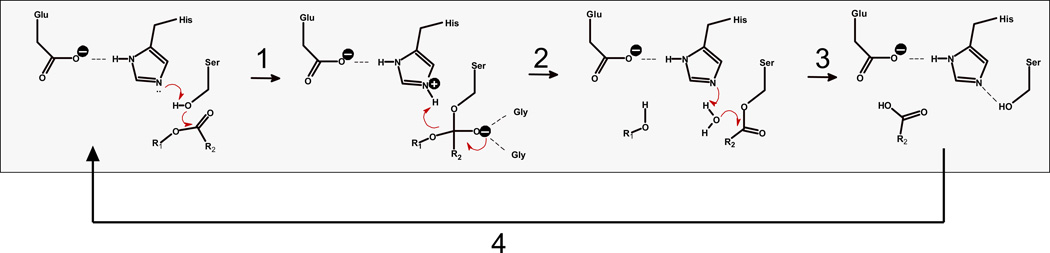
Figure 1.
Catalytic cycle of CES-mediated hydrolysis of ester substrates. Step 1. Nucleophilic attack of serine Oγ on carbonyl carbon of ester substrate R2-C(=O)-OR1 and formation of tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate, which is stabilized by the oxyanion hole. Serine Oγ is activated by charge relay complex established between the Glu-His-Ser catalytic triad residues. Step 2. Collapse of oxyanion intermediate and formation of acyl-enzyme covalent intermediate and alcohol product, R1OH. Step 3. Acyl-enzyme intermediate is attacked by a water molecule, which is activated by the catalytic His residue, thereby liberating the carboxylic acid product, R2-C(=O)-OH. Step 4. Catalytic triad hydrogen bond network re-establishes itself and cycle repeats.