Table 3.
Characteristics of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from cattle feces and environmental samples in Gyeonggi-do, Korea
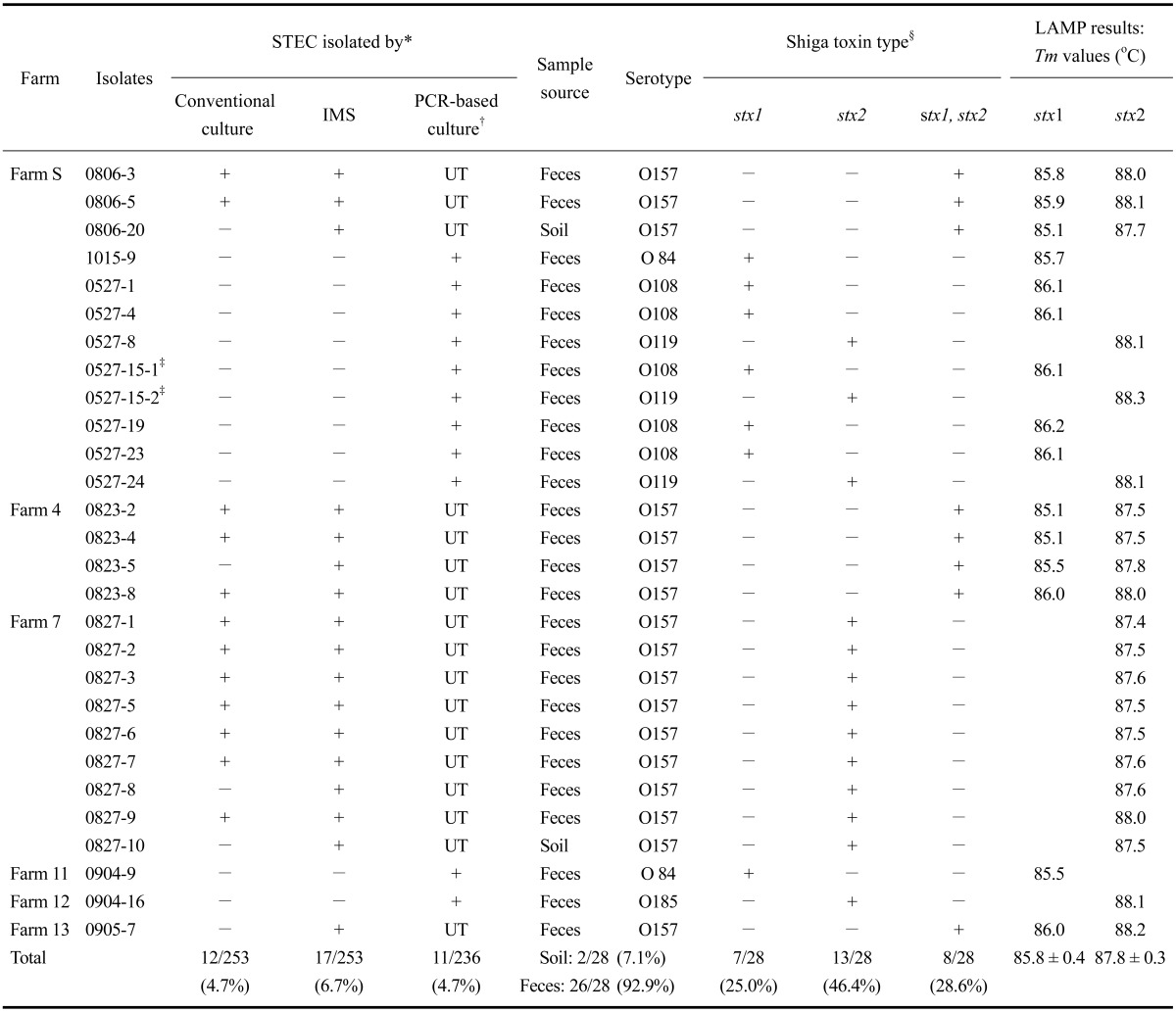
*Twenty-eight STEC strains were isolated from a total of 253 cattle farm samples from 15 enrolled cattle farms by three different methods. For isolation of STEC O157, a conventional culture method based on SMAC agar media was used; while immunomagnetic beads coated with anti-O157 were used for the immunomagnetic separation (IMS) method. †A polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based culture method was used for isolation of non-O157 STEC strains. From a total of 253 samples, 17 STEC-O157 positive samples were excluded from the PCR assay. ‡Two strains with different serotypic and genotypic characterizations were isolated from the same sample. §Shiga toxin types were determined by mPCR and the mLAMP assay, which were concordant. UT: untested.
