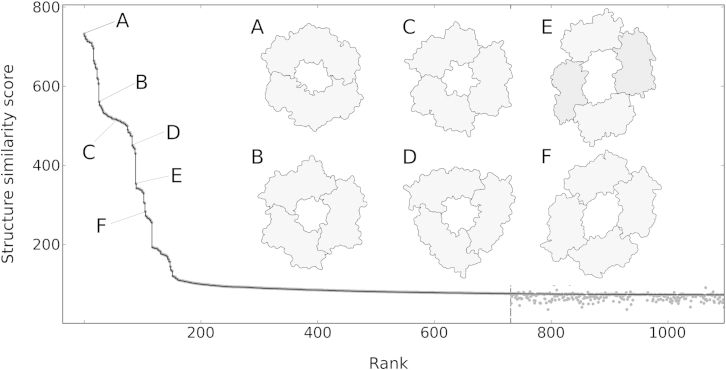
Figure 3.
A Structure Search with a Dimeric Bacterial DNA Clamp against All Known Biological Assemblies Reveals Different Types of Ring-like DNA Polymerase Subunits
The set of all biological assemblies (138,602 items; November 19, 2013) is searched for structures similar to a dimeric bacterial DNA clamp (2pol@; Kong et al., 1992). Structure similarity scores S and ranks are plotted for the top 1,100 hits (black line). Structure similarities below the threshold of S+ = 75.1 (dashed vertical line) are approximate (gray dots; Experimental Procedures). The dimeric bacterial clamp matches various ring-like assemblies, six of which are schematically shown and linked to their respective positions in the hit list. (A) 2pol@1 (homodimer; Kong et al., 1992). (B) 1plr@1 (homotrimer; Krishna et al., 1994), a proliferating cell nuclear antigen from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. (C) 3hi8@1 (homotrimer; Morgunova et al., 2009), a proliferating cell nuclear antigen from Haloferax volcanii. (D) 1czd@1 (homotrimer; Moarefi et al., 2000), a DNA polymerase accessory protein from Enterobacteria phage T4. (E) 3aiz@1 (heterotetramer; Kawai et al., 2011), a DNA polymerase sliding clamp from Sulfolobus tokodaii. (F) 2z0l@8 (homotetramer; Murayama et al., 2009), a DNA polymerase processivity factor from human herpesvirus 4.