Figure 2.
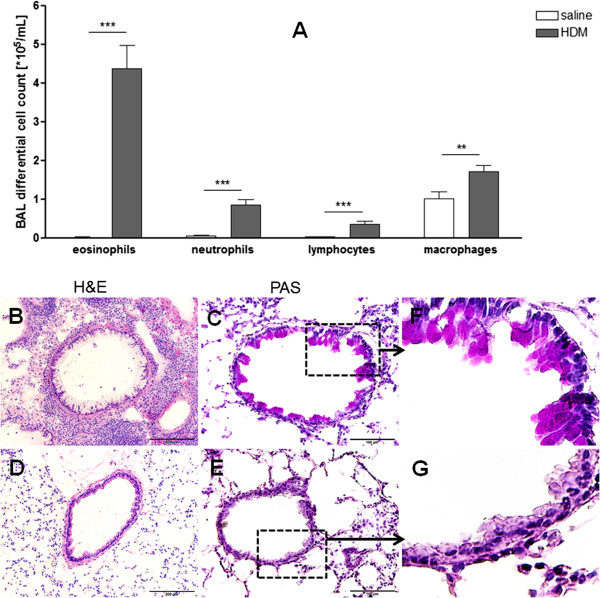
The inflammatory response in the lungs observed after continuous expose to HDM. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) cells differentiation (A). Eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes and macrophages in BALF demonstrated inflammation in the lungs of HDM-exposed mice, in comparison with control mice. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (unpaired two-tailed t-test). Representative photomicrographs of H&E (B,D,G) and PAS (C,E,F) stained lung sections. The lung sections from HDM-sensitised and challenged mice showed an infiltration of mononuclear cells (B) and a highly mucus secretion (C) in the airways, whereas the lungs of the control mice do not contain aggregated inflammatory cells (D) and mucus secretion (E). F and G: larger magnifications of C and E. Scale bars of B and D: 200 μm, scale bars of C and E: 100 μm.
