Figure 1.
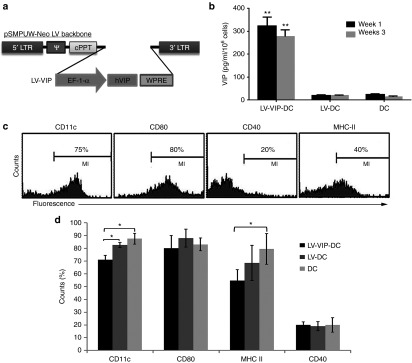
Generation and characterization of LV-VIP-DC. (a) Schematic representation of the LV cassette carrying VIP gene (LV-VIP). EF-1α promoter drives expression of hVIP cDNA in pSMPUW-Neo LV plasmid. (b) VIP secretion by LV-VIP–transduced dendritic cells (LV-VIP-DCs). LV-VIP-DCs and controls were cultured at a concentration of 1 × 106 cells/well for 24 hours, and the culture supernatant was analyzed for VIP levels using enzyme-immunoassay method. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM) of four experiments. LV-DC, DCs transduced LV without hVIP cDNA. (c) Flow cytometry showing LV-VIP-DCs–expressing phenotypic markers, CD11c, CD80, CD40, and MHC-II at 3–4-day post-transduction. (d) Quantification of phenotypic markers, LV-VIP-DCs versus controls. Error bars represent SEM of five experiments. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. cPPT, central polypurine tract; DC, dendentric cell; EF, elongation factor; hVIP, human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide; LTR, long terminal repeat; LV, lentiviral vector; VIP, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide; WPRE, woodchuck hepatitis post-transcriptional regulatory element; ψ, cis acting elements.
