Figure 2.
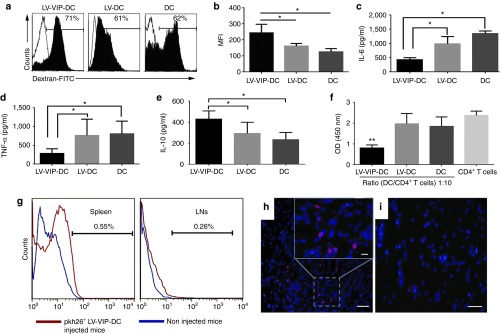
Functional characteristics and in vivo tracking of LV-VIP-DCs. (a) Endocytic capacity of LV-VIP-DCs and controls was determined 4–5 days after transduction by incubating the cells with 1 mg/ml dextran-FITC in medium for 3 hours at 4 °C (control; open histograms) or 37 °C (filled histograms) and analyzed by flow cytometry. (b) MFI were shown. LV-VIP-DCs were exposed to 1 µg/ml LPS in medium for 48 hours. The culture supernatant analysis shown at 24 hours for (c) IL-6, (d) TNF-α and at 48 hours for (e) IL-10. (f) LPS-induced LV-VIP-DCs, LV-DCs, and DCs were cocultured with splenic CD4+ T cells (2 × 105 cells/well) isolated from spontaneous autoimmune peripheral polyneuropathy (SAPP) mice in a 96-well plate in the presence of 5 µg/ml phytohemagglutinin and 50 U/ml IL-2 for 48 hours. Cell proliferation was determined by performing colorimetric BrdU cell proliferation assay. For b–f, the error bars represent standard error of the mean of three experiments done in triplicates; statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. (g) Pkh26-labeled LV-VIP-DCs (3 × 106 cells) were injected into SAPP mice at 24 weeks of age (n = 5) and were detected in spleens and LNs at 48-hour postinjection by using flow cytometry. Sciatic nerves were removed 48-hour postinjection. Twelve-micrometer-thick cross-sections of sciatic nerve, which were viewed under fluorescent microscope, showed the presence of pkh26-labeled LV-VIP-DCs in the injected mice (h). (i) Sciatic nerve of noninjected mouse (scale bar = 50 µm; insert scale bar =10 µm). BrdU, 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine; DC, dendentric cell; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; IL, interleukin; LNs, lymph nodes; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LV, lentiviral vector; MFI, mean fluorescence intensities; pkh26, red fluorescent dye; VIP, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide.
