Fig. 1.
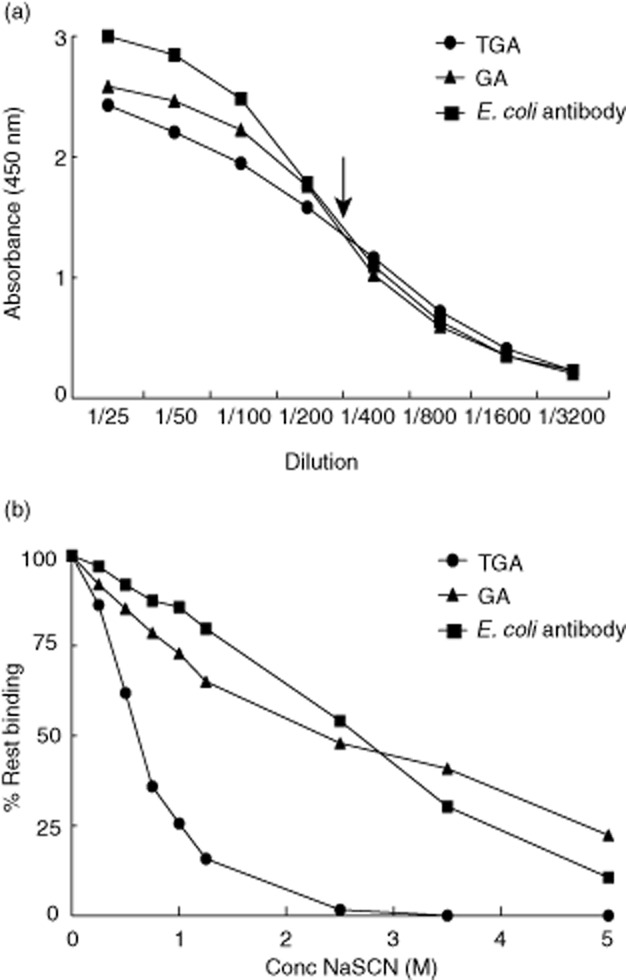
Titration of serum and sodium thiocyanate (NaSCN). (a) Serum of one patient was chosen as an example and titrated in the three different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs): for immunoglobulin (Ig)A transglutaminase-2 (TG2) antibodies (TGA), for IgA Escherichia coli antibodies and for IgA gliadin antibodies (GA). The dilution, resulting in 50% binding, was chosen to use in the avidity ELISA (indicated by the arrow). The dilution is shown on the x-axis and the absorbance at λ = 450 nm at the y-axis. (b) The same serum as in (a) was used at 50% of the maximum dilution (= 1/400) and NaSCN was titrated from 0 to 5 M (x-axis) to obtain the salt concentration that provides the most information on avidity differences (= 1 M). Avidity is expressed as the percentage of rest binding (y-axis), which is the (concentration of antibody after NaSCN elution/concentration of antibody without elution) × 100. The concentrations were calculated using a standard line and expressed arbitrarily as U/ml.
