Fig. 9.
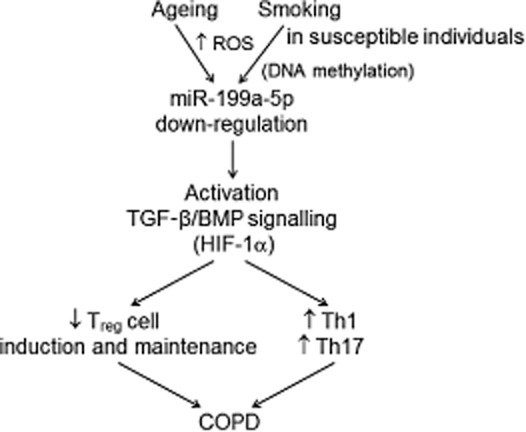
A schematic of the proposed function of miR-199a-5p in regulatory T cells (Treg). Deregulation of miR-199a-5p due possibly to the increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) leads eventually to an over-expression of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β/bone morphogenic protein (BMP) signalling pathway, thus skewing the T cell response to T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th17 cells. As we found a positive correlation between miR-199a-5p expression and age, it is also possible that any of the aberrant ageing mechanisms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be involved in the deregulation of miR-199a-5p.
