Fig. 5.
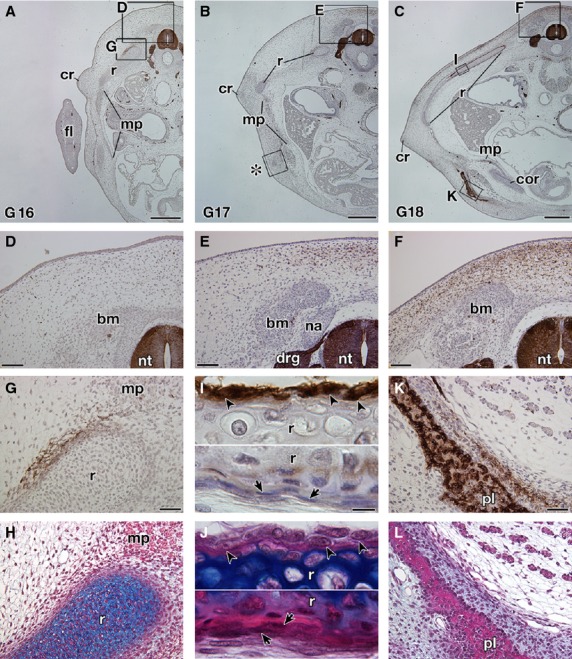
Expression of the HNK-1 epitope in Trachemys scripta embryos. Transverse sections of T. scripta embryos are either stained with HNK-1 and counterstained with hematoxylin (A–G,I,K) or simply stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and then Alcian blue (H,J,L). (A–C) Transverse sections at low magnification. (D–L) Higher magnification of the boxes in (A–C). (H,J, L) Adjacent sections to (G,I,K), respectively. (D–F) The dorsal part of the embryo showing the distribution of the HNK-1 epitope. Note that the HNK-1 epitope appears from G stage 17 (E) and the expression domain expands in G stage 18 (F). (G–J) Distribution of the HNK-1 epitope in the ribs. A part of the mesenchyme surrounding the ribs is HNK-1-positive (G,H). In G stage 18 (I,J), the epitope was observed in the cells with a round nucleus in the periosteum (arrowheads), whereas the cells with a long nucleus are HNK-1-negative (arrows). (K,L) Distribution of the HNK-1 epitope in the plastron of the G stage 18 embryo. Immunoreactivity was observed for the osteoblast in the plastral bones and in the adjacent mesenchyme. drg, dorsal root ganglion; fl, fore limb; na, neural arch; nt, neural tube. Scale bars: 500 μm (A–C), 100 μm (D–F), 50 μm (G,H,K,L), 20 μm (I,J).
