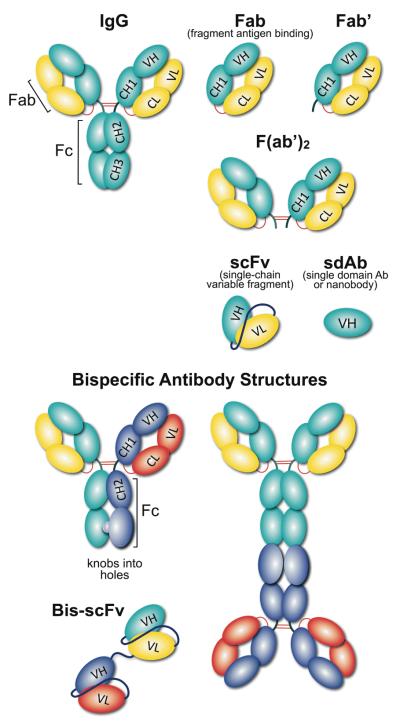
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of different antibody formats. An array of recombinant antibody formats were developed using combinations of antibody domains, joined either with linkers and/or disulfide bonds. Using molecular biology tools, antibody valency and specificity can be tailored into monovalent (sdAb (single domain Ab); Fab and Fab’ (fragment antigen binding), divalent (F(ab’)2) and even multivalent formats. Formats with antibody constant domains are highly stable, however, single chain antibody formats are popular due to their small size, expression and tissue penetration capabilities. Linker length can also influence the antibody behavior in terms of stability, flexibility and aggregation. A bispecific antibody is a recombinant antibody format that recognize two distinct antigens, using two IgG or scFv, linked together either chemically by covalent conjugation; or genetically with peptide linkers; or disulfide bonds.