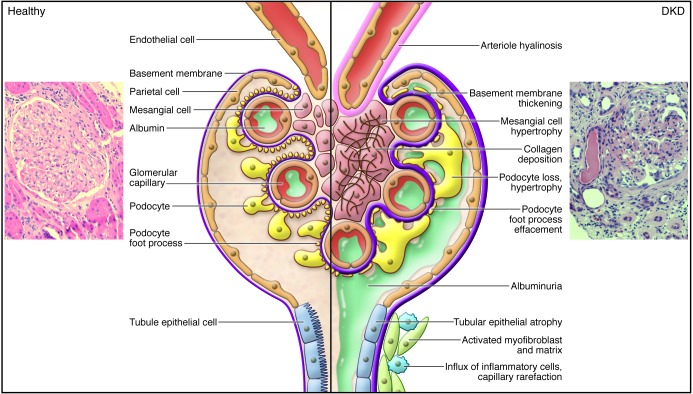
Figure 1. Pathological lesions of DKD.
The normal healthy glomerulus includes afferent arterioles, capillary loops, endothelial cells, basement membrane, podocytes, parietal epithelial cells, and tubule epithelial cells and is impermeable to albumin. In contrast, the diabetic glomerulus displays arterial hyalinosis, mesangial expansion, collagen deposition, basement membrane thickening, podocyte loss and hypertrophy, albuminuria, tubular epithelial atrophy, accumulation of activated myofibroblasts and matrix, influx of inflammatory cells, and capillary rarefaction. Also shown are a normal healthy human glomerular section and a kidney section from a sample with DKD (PAS stained). Original magnification, ×400.