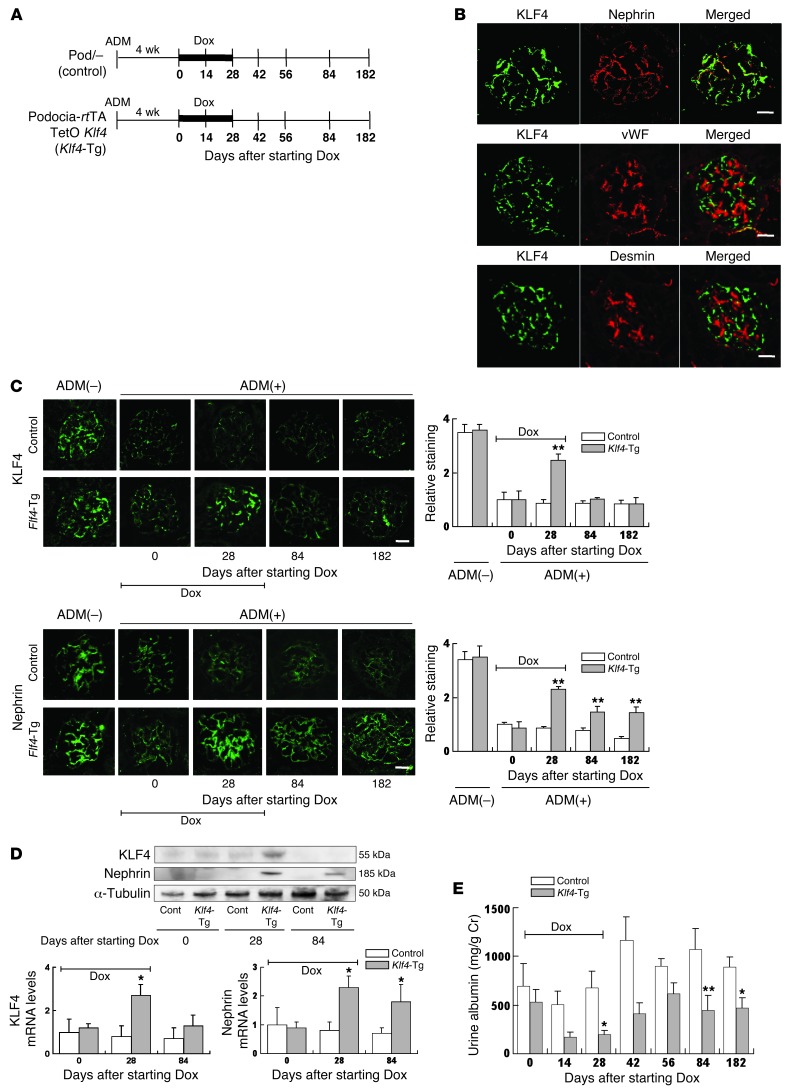
Figure 2. Restoration of podocyte KLF4 expression in diseased glomeruli attenuates proteinuria.
(A) Experimental protocol using Dox-inducible podocyte-specific Klf4 transgenic mice (podocin-rtTA TetO Klf4) and controls (podocin-rtTA [Pod/–]). Dox was administered for 28 days to induce KLF4 expression as indicated, and mice were sacrificed at days 0, 28, 84, and 182 after starting Dox (n = 5–6 per time point). (B) Immunofluorescence double staining of KLF4 (green) together with nephrin (red), vWF (red), or desmin (red) in Klf4 transgenic mice kidneys after 28 days Dox treatment. (C) (Left panel) Representative confocal photomicrographs and (right panel) quantification of glomerular KLF4 and nephrin expression without ADM treatment or at the indicated days after starting Dox in ADM nephropathy of Klf4 transgenic mice or controls. (D) (Upper panel) Western blot and (lower panel) real-time RT-PCR analysis of KLF4 and nephrin expression in the kidney cortex of Klf4 transgenic mice or controls at the indicated times after starting Dox treatment. (E) Quantification of albuminuria in Klf4 transgenic mice and controls at the indicated times after starting Dox treatment. Control: results for control mice (Pod/–); Klf4-Tg: results for podocyte-specific Klf4 transgenic mice (podocin-rtTA TetO Klf4). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 vs. Pod/– controls. Scale bars: 25 μm.