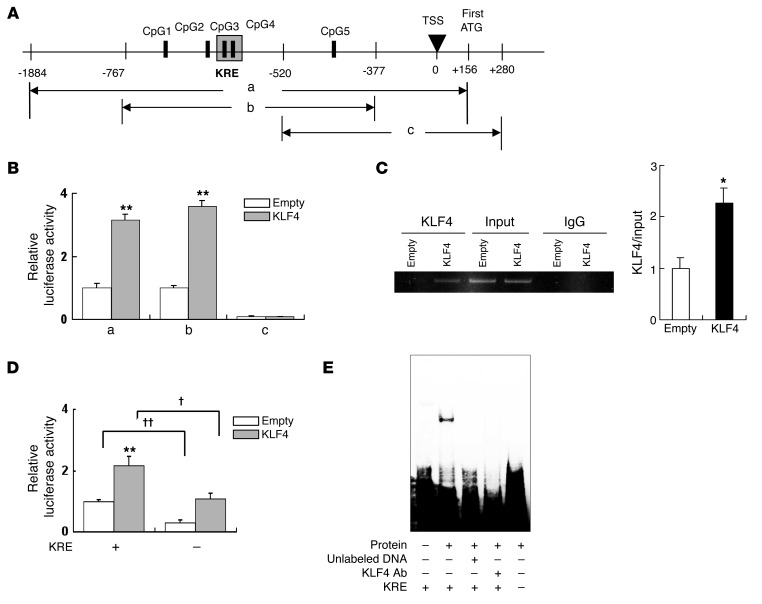
Figure 8. KLF4 expression increases nephrin promoter activity in podocytes.
(A) Map of nephrin promoter regions included in the luciferase constructs. CpG 1–5 correspond to the sites shown in Supplemental Figure 8. (B) Luciferase activity 48 hours after transfection of KLF4-overexpressing podocytes (KLF4) or control podocytes (empty) with constructs containing regions a–c (n = 6). (C) ChIP assay for the presence of KLF4 in the promoter region of nephrin in KLF4-overexpressing podocytes (KLF4) or control podocytes (empty). The amplified fragment corresponds to region B in Figure 8A. The bar graph shows the quantification of KLF4/input intensity (n = 4). (D) Effect of KRE deletion on nephrin promoter activity. Luciferase activity was assayed 48 hours after transfection of luciferase constructs containing region B with (KRE[–]) or without (KRE[+]) specific deletion of the KRE (shown boxed in the upper panel of Supplemental Figure 8) into KLF4-overexpressing podocytes or control podocytes (n = 6). (E) Effect of KRE deletion on DNA binding to podocyte nuclear extracts analyzed by EMSA. Nuclear extracts from KLF4-overexpressing podocytes were pretreated with or without unlabeled competitor DNA or KLF4 antibody before incubation with labeled probes for EMSA to confirm specificity of the complexes. KRE (–) and (+) refer to probes with or without a deletion of the KRE sequence, respectively. **P < 0.01 vs. controls. †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 vs. the respective groups.