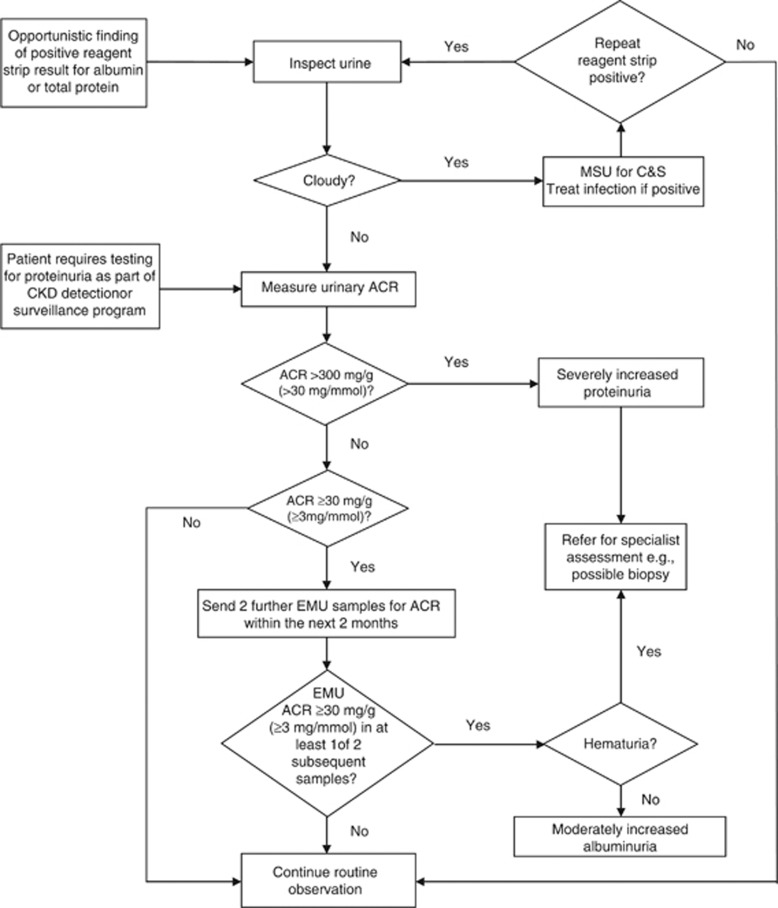
Figure 16.
Suggested protocol for the further investigation of an individual demonstrating a positive reagent strip test for albuminuria/proteinuria or quantitative albuminuria/proteinuria test. Reagent strip device results should be confirmed using laboratory testing of the ACR on at least two further occasions. Patients with two or more positive (≥30 mg/g or ≥3 mg/mmol) tests on early morning samples 1-2 weeks apart should be diagnosed as having persistent albuminuria. The possibility of postural proteinuria should be excluded by the examination of an EMU. PCR measurement can be substituted for the ACR but is insensitive in the detection of moderately increased albuminuria/proteinuria. Approximate PCR equivalent to an ACR of 30 mg/mmol is 50 mg/mmol. ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; C&S, culture and sensitivity; CKD, chronic kidney disease; EMU, early morning urine; MSU, mid-stream urine; PCR, protein-to-creatinine ratio. aConsider other causes of increased ACR (e.g., menstrual contamination, uncontrolled hypertension, symptomatic urinary tract infection, heart failure, other transitory illnesses, and strenuous exercise), especially in the case of type 1 diabetes present for less than 5 years. The presence of hematuria may indicate non-diabetic renal disease. This figure was published and adapted from Lamb EJ, Price CP.122 Kidney function tests, in Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, eds Burtis CA, Ashwood E, Bruns DE, 5th edition, pp 669-708, 2012. Copyright Elsevier.